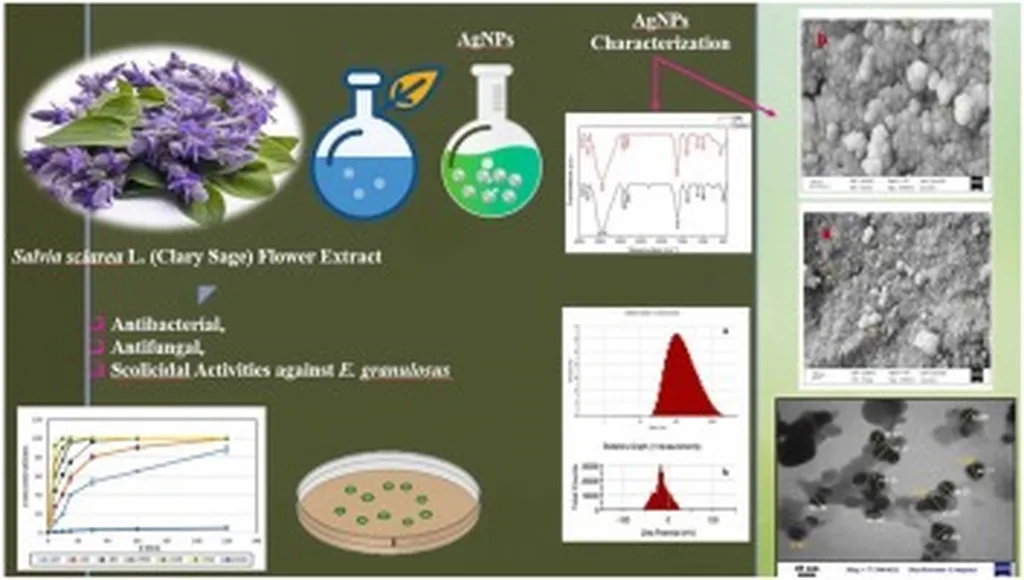
In the heart of Istanbul, a groundbreaking study led by Elif Arslan at Yildiz Technical University is reshaping our understanding of green synthesis and its potential to revolutionize the energy sector. The research, published in Nano Express, focuses on the environmentally friendly production of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using clary sage (Salvia sclarea L.), a plant known for its medicinal properties. This innovative approach not only offers a sustainable alternative to conventional chemical methods but also opens doors to enhanced secondary metabolite production and antimicrobial applications.
The study highlights the synthesis of AgNPs using clary sage leaf extract as a reducing and stabilizing agent. “The use of plant extracts in nanoparticle synthesis is gaining traction due to its eco-friendly nature and cost-effectiveness,” Arslan explains. The resulting nanoparticles exhibited a characteristic surface plasmon resonance peak at ~449 nm, confirming their formation. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed a face-centered cubic crystalline structure, while transmission electron microscopy showed spherical nanoparticles ranging from 2.4 to 30.6 nm, with an average size of 12.9 nm.
One of the most intriguing findings of the study is the impact of AgNPs on the secondary metabolite profile of clary sage tissue culture media. The incorporation of AgNPs significantly altered the metabolite composition, with fatty acid and n-alkane derivatives emerging as dominant groups. “This suggests that AgNPs can act as elicitors, enhancing the production of valuable secondary metabolites,” Arslan notes. The main compounds identified were octadecanic acid, nonacosene, heptacosene, and dotriacontane, which have potential applications in various industries, including agriculture and pharmaceuticals.
The antimicrobial activity of the AgNPs was also evaluated against common bacterial strains, including Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. The results were promising, with the AgNPs exhibiting moderate antimicrobial properties. This finding underscores the potential of AgNPs in combating bacterial pathogens, a critical area of concern for the energy sector, particularly in maintaining the integrity of biofuels and other bioproducts.
The study’s emphasis on green synthesis and its multifaceted applications holds significant promise for the energy sector. By utilizing environmentally friendly methods, the research paves the way for sustainable production of nanoparticles with enhanced properties. “The potential to enhance secondary metabolite production and counteract microbial threats is a game-changer,” Arslan states. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact but also offers cost-effective solutions for various industrial applications.
As the world increasingly turns to sustainable and green technologies, the research led by Elif Arslan at Yildiz Technical University stands out as a beacon of innovation. The study, published in Nano Express (translated to English as “Nano Express”), highlights the potential of clary sage-mediated synthesis of AgNPs to revolutionize the energy sector. By combining the principles of green chemistry with advanced nanotechnology, this research opens new avenues for sustainable development and industrial applications. The findings not only advance our understanding of nanoparticle synthesis but also underscore the importance of integrating natural resources into modern technological solutions.