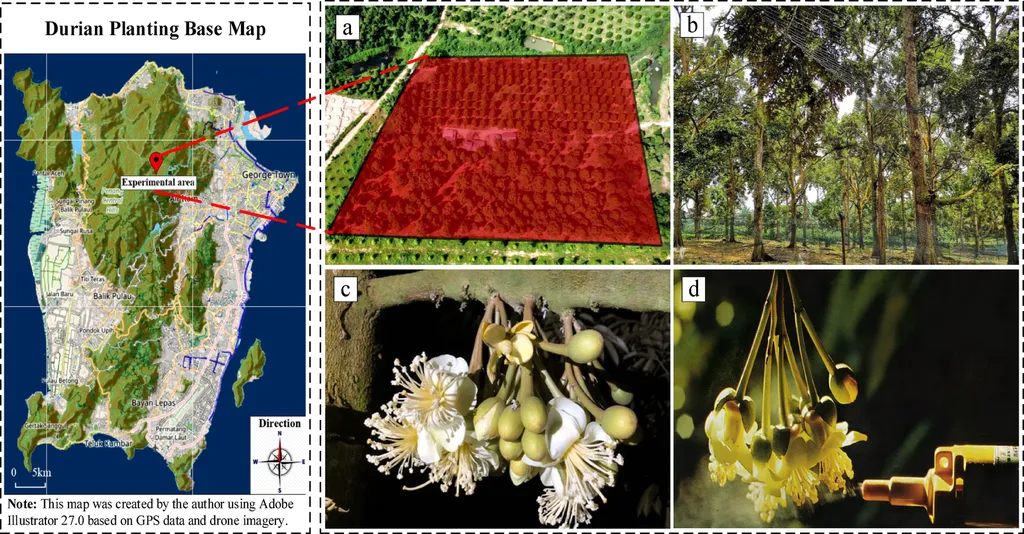
In the heart of tropical agriculture, a groundbreaking study led by Ruipeng Tang from the School of Electrical, Electronic and Mechanical Engineering at the University of Bristol is revolutionizing the way we think about pollination. The research, published in *Scientific Reports* (translated to English as *Scientific Reports*), introduces an AI-powered drone-based pollination method that promises to transform the durian industry, a sector worth billions globally.
Durian, often dubbed the “king of fruits,” is a labor-intensive crop that relies heavily on natural pollinators like bats and nocturnal insects. However, environmental degradation and pesticide use have significantly reduced these pollinator populations, leading to inefficient natural pollination. This is where Tang’s innovative solution comes into play. “Our method integrates improved object detection and optimized path planning to create a more efficient and reliable pollination process,” Tang explains.
The study enhances the YOLO-v8 algorithm using the GhostNet lightweight network, reducing computational complexity while boosting detection precision. This improvement is crucial for navigating the complex environments of durian orchards, where low-light and occluded conditions can challenge traditional detection methods. “The novel use of GhostNet with YOLO-v8 enables superior detection of durian flowers under these challenging conditions,” Tang adds.
For path planning, the researchers developed an Enhanced TSP (EN-TSP) algorithm based on a branch and bound strategy with least-cost optimization. This ensures globally optimal drone routes, reducing travel distance and improving operational reliability. The results are impressive: the proposed method improves detection accuracy by 5.85% and path efficiency by 26.89% compared to baseline algorithms.
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. Durian is a high-value crop, and any improvement in yield and quality can have a significant impact on the agricultural sector. By automating the pollination process, farmers can reduce labor costs and increase productivity. “This integrated solution advances smart agriculture by enabling scalable, efficient, and precise pollination,” Tang notes.
The potential applications extend beyond durian orchards. The technology could be adapted for other crops that rely on natural pollinators, offering a sustainable solution to the challenges posed by environmental degradation and pesticide use. As the agricultural sector continues to evolve, the integration of AI and drone technology is likely to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of farming.
This research not only highlights the potential of AI and drone technology in agriculture but also underscores the importance of innovation in addressing the challenges faced by the agricultural sector. As we look to the future, the integration of these technologies is set to revolutionize the way we approach farming, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient agricultural industry.