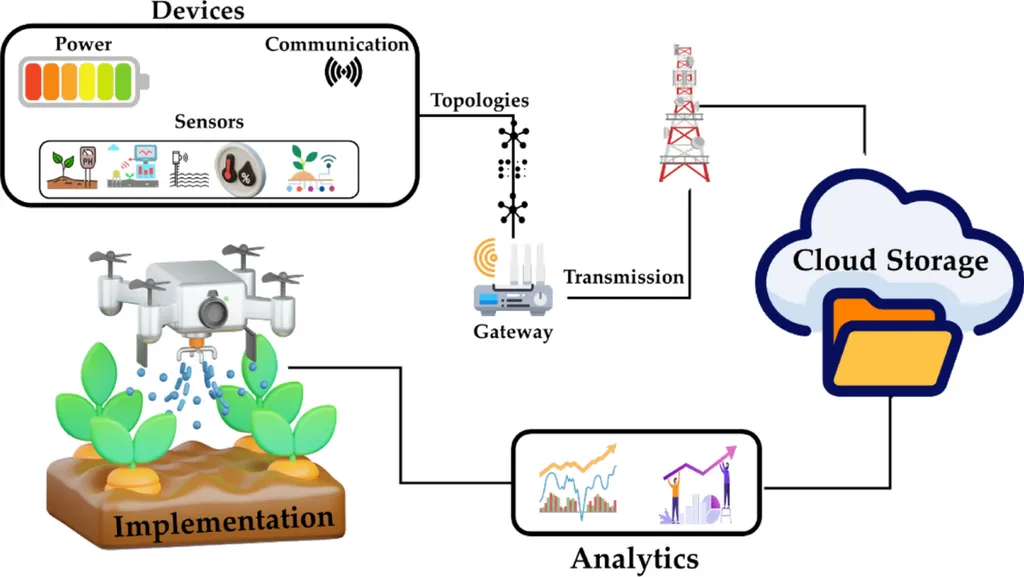
In the vast, often overlooked expanses of rural and remote areas, the Internet of Things (IoT) is quietly revolutionizing agriculture and infrastructure management. Yet, these regions present unique challenges that can stifle the potential of connected devices. A recent study published in the IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society delves into these hurdles, offering a comprehensive review of real-time data transfer and energy consumption strategies tailored for these environments.
The research, led by Seyed Nooreddin Jafari from the Computer Science Department at the University of Beira Interior in Portugal, highlights the critical need for low-latency connectivity and sustainable energy consumption in rural IoT deployments. “Intermittent connectivity, geographical barriers, and limited device power budgets are significant obstacles,” Jafari explains. “These challenges raise substantial difficulties in implementing technology in such environments.”
The study underscores that as communication technologies become more prevalent in remote areas, the reliance on connected devices for activities like agriculture and infrastructure management grows. However, the natural constraints of these regions demand innovative solutions for real-time communication and energy efficiency.
The survey meticulously examines state-of-the-art solutions addressing real-time data transmission and energy efficiency. It identifies key research gaps, offering valuable insights for researchers, practitioners, and policymakers. “By studying communication protocols and power management, we aim to provide a roadmap for IoT deployment in resource-constrained environments,” Jafari notes.
For the agriculture sector, the implications are profound. Real-time data transfer enables precision farming, allowing farmers to monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns with unprecedented accuracy. This data-driven approach can lead to increased yields, reduced resource waste, and improved sustainability. Moreover, efficient energy consumption strategies ensure that these devices can operate autonomously, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing reliability.
The research also explores various communication methods, including wireless sensors and satellite communication, which are crucial for overcoming geographical barriers. These technologies can bridge the connectivity gap, ensuring that rural and remote areas are not left behind in the digital revolution.
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and food security, the role of IoT in agriculture becomes increasingly vital. This study not only sheds light on the current state of rural IoT deployments but also paves the way for future developments. By addressing the critical challenges of real-time data transfer and energy consumption, it offers a blueprint for a more connected, efficient, and sustainable agricultural future.
The findings, published in the IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society and led by Seyed Nooreddin Jafari from the University of Beira Interior, serve as a catalyst for further research and innovation in this field. As we move forward, the insights gained from this study will be instrumental in shaping the future of IoT in rural and remote areas, ultimately benefiting the agriculture sector and beyond.