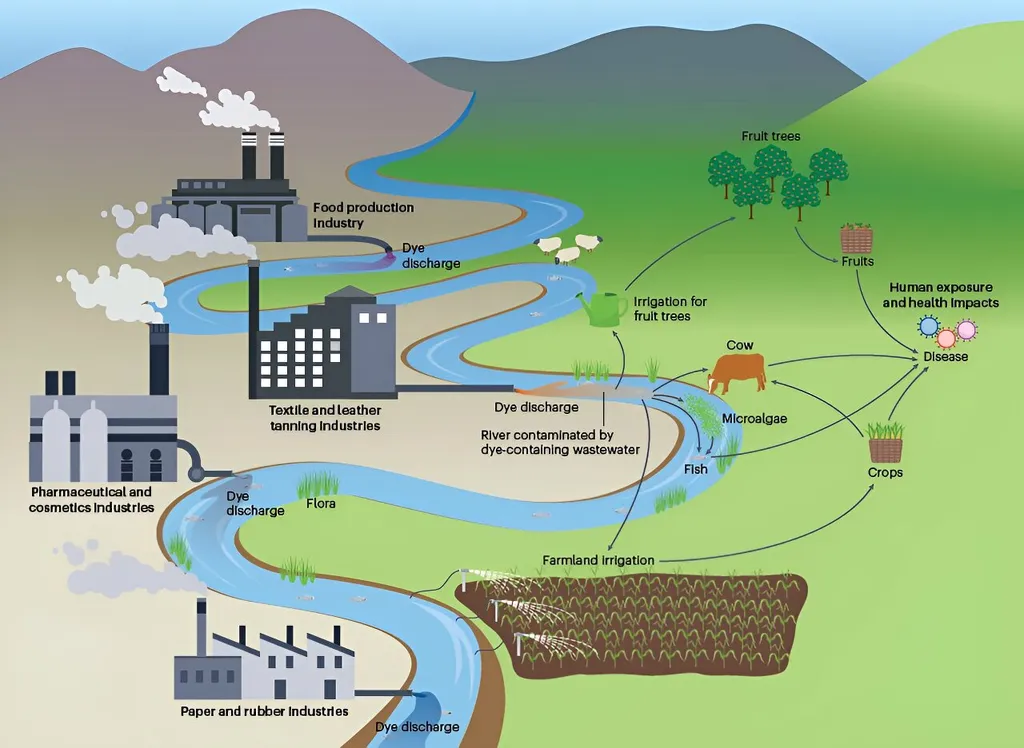
In the quest for cleaner water, scientists are turning to innovative solutions to tackle persistent pollutants. A recent comprehensive review published in *Sustainable Chemistry for the Environment* sheds light on the adsorption of Eriochrome Black T (EBT), a dye notorious for its toxicity and persistence in aquatic environments. The study, led by Joshua O. Ighalo from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Nnamdi Azikiwe University in Nigeria, consolidates findings from over 50 research papers to evaluate the efficiency and sustainability of various adsorbents in removing EBT from water.
EBT, commonly used in textiles and dyes, poses significant threats to aquatic ecosystems and human health. Its removal is crucial for environmental protection, and adsorption-based techniques have emerged as a promising solution. The review reveals that EBT uptake is predominantly described by the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetics, with mechanisms involving electrostatic attraction, hydrogen bonding, and π–π interactions.
“Adsorption is a cost-effective and scalable method for EBT removal,” states Ighalo. “However, challenges remain, including high production costs of advanced adsorbents and reduced efficiency after repeated regeneration.”
The study highlights that several adsorbents maintain over 80% capacity after five regeneration cycles, indicating their potential for repeated use. Yet, the high production costs of advanced adsorbents and their reduced efficiency after repeated use pose significant hurdles. The review calls for future research to focus on developing low-cost, sustainable materials and improving regeneration efficiency.
For the agriculture sector, the implications are substantial. Water contamination by dyes can severely impact irrigation systems and agricultural productivity. Effective removal of EBT and similar pollutants can lead to cleaner water sources, enhancing crop yields and ensuring food safety. Moreover, the development of low-cost adsorbents can make water treatment more accessible to rural and agricultural communities, fostering sustainable farming practices.
The study also emphasizes the need for pilot- and industrial-scale applications, comprehensive life cycle and techno-economic analyses, and the integration of regulatory and policy frameworks. These steps are essential for the practical and sustainable implementation of adsorption techniques in water treatment.
As the world grapples with increasing water pollution, this research offers a beacon of hope. By advancing adsorption technologies, we can pave the way for cleaner water and a healthier environment, ultimately benefiting agriculture and beyond. The findings underscore the importance of continued research and innovation in water treatment technologies, ensuring a sustainable future for all.