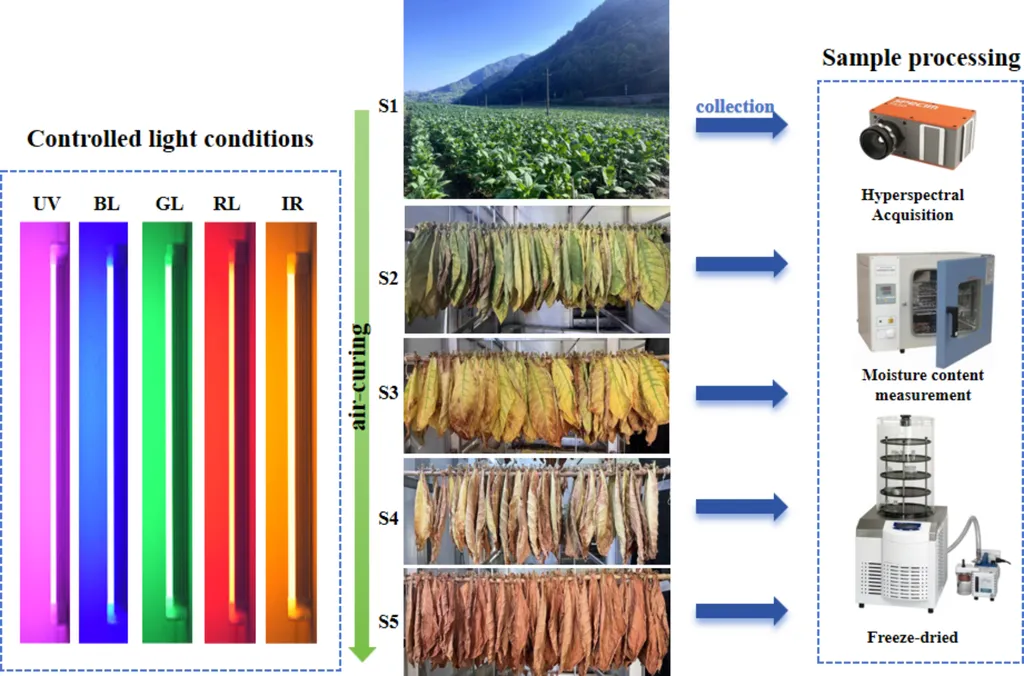
In the ever-evolving landscape of agricultural technology, a groundbreaking study has emerged that promises to revolutionize the way we assess the quality of cured tobacco leaves. Published in the journal *Industrial Crops and Products*, the research introduces an intelligent prediction framework that combines hyperspectral imaging (HSI) with a deep neural network model enhanced by dual-attention modules. This innovation could significantly impact the tobacco industry by providing rapid and reliable quantification of nicotine levels, a critical factor in tobacco processing.
The study, led by Fukang Xing of the Tobacco Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Shihezi University, employs a multi-region spectral acquisition strategy to capture representative reflectance data from different areas of tobacco leaves. This approach ensures that the data collected is comprehensive and representative, addressing a longstanding challenge in the industry.
One of the most notable aspects of this research is the development of a Dual-Attention-enhanced CNN-LSTM (DACL) model. This model incorporates a Band Attention (BA) module for adaptive spectral band selection and a Self-Attention (SA) module for deep feature refinement. According to Xing, “The fusion of spectral and deep feature attention within a CNN-LSTM architecture provides a robust and interpretable solution for real-time nicotine assessment in cured tobacco.”
The DACL model was trained on multi-region averaged spectra and evaluated against classical machine learning models (PLSR, SVR) and deep learning baselines (CNN, LSTM, CNN-LSTM). The results were impressive, with the DACL approach achieving an R² of 0.857, an RMSE of 0.443, and an RPD of 2.642 on the independent test set. These metrics indicate a high level of accuracy and reliability, making the DACL model a promising tool for quality control in tobacco processing.
The visualization of the attention modules confirmed that the model consistently prioritized wavelengths corresponding to nicotine’s characteristic absorption bands. This not only enhances predictive accuracy but also provides interpretability, a crucial factor for practical application in the field.
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. Rapid and reliable quantification of nicotine levels can lead to more efficient processing, reduced waste, and improved product quality. This, in turn, can enhance the competitiveness of tobacco products in the global market. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of AI-driven hyperspectral analysis could become a standard practice, benefiting not only the tobacco sector but also other areas of agriculture.
The study highlights the broader potential of AI-driven hyperspectral analysis in agricultural product evaluation. As Fukang Xing notes, “The proposed method offers new insights for quality control in tobacco processing and underscores the importance of leveraging advanced technologies to enhance agricultural practices.”
In conclusion, this research represents a significant step forward in the field of agricultural technology. By combining hyperspectral imaging with deep learning and attention mechanisms, the study provides a robust and interpretable solution for real-time nicotine assessment in cured tobacco. The implications for the agriculture sector are far-reaching, and the potential for future developments in this area is immense. As the industry continues to embrace advanced technologies, the integration of AI-driven hyperspectral analysis could become a game-changer, shaping the future of agricultural product evaluation.