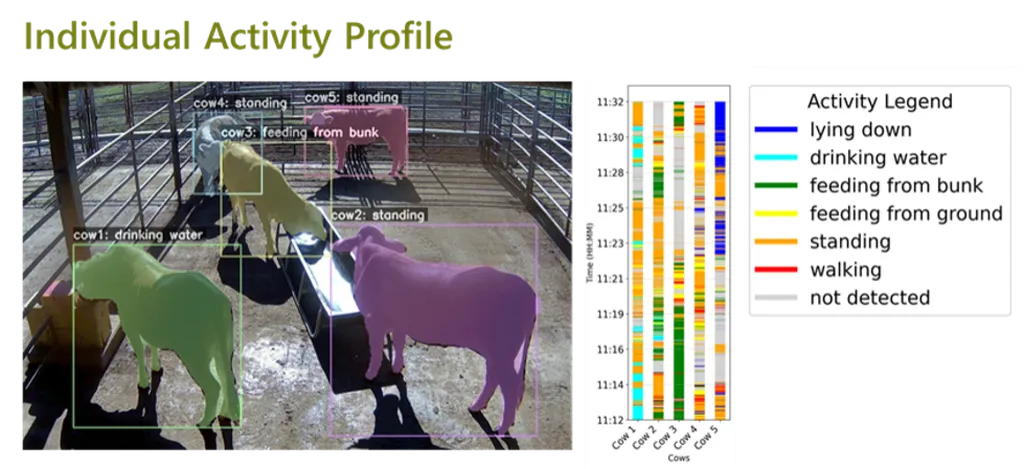
In the rapidly evolving world of precision agriculture, data is king. And for cattle farmers, the ability to harness this data to understand and predict animal behavior could revolutionize farm management. A recent study published in the journal *Sensors* offers a promising new approach to this challenge, using advanced statistical modeling to turn complex sensor data into actionable insights.
The research, led by Yukie Hashimoto from the Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Agriculture and Engineering at the University of Miyazaki in Japan, introduces a novel Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulation model. This model is designed to analyze data from multiple sensors, including 3D acceleration, pneumatic, and proximity sensors, to generate accurate activity patterns for cattle.
“Our goal was to create a robust tool that could process diverse sensor inputs and provide reliable behavioral patterns,” Hashimoto explained. “By doing so, we aimed to offer farmers a data-driven approach to optimize key aspects of their operations.”
The implications for the agriculture sector are significant. The study demonstrates that the MCMC simulation can directly impact several critical areas of farm management. For instance, by understanding cattle activity patterns, farmers can optimize feed allocation, ensuring that each animal receives the right amount of nutrition at the right time. This not only improves animal health and productivity but also reduces waste and costs.
Early disease detection is another area where this technology could make a substantial difference. By identifying subtle changes in behavior that might indicate illness, farmers can intervene sooner, potentially saving lives and preventing the spread of disease within the herd.
Moreover, the model can aid in labor scheduling. By predicting periods of high activity, farmers can allocate labor resources more efficiently, ensuring that there are always enough hands on deck during critical times.
The research validates its approach through a combination of controlled monthly experiments and the analysis of real-world data. The results confirm that the MCMC simulation can effectively process diverse sensor inputs to generate reliable and detailed behavioral patterns.
“This data-driven methodology provides significant advantages for developing informed management strategies,” Hashimoto noted. “It leads to improvements in the overall efficiency, productivity, and profitability of cattle operations.”
Looking ahead, this research could shape future developments in precision livestock farming. As sensor technologies continue to advance and become more affordable, the ability to integrate and analyze this data will become increasingly important. Advanced statistical models like MCMC could play a pivotal role in this process, transforming raw data into tangible improvements for modern agriculture.
In an industry where margins can be tight and uncertainties abound, tools that offer greater predictability and control are invaluable. This study represents a significant step forward in that regard, offering a glimpse into a future where data and technology work hand in hand to enhance the productivity and sustainability of cattle farming.