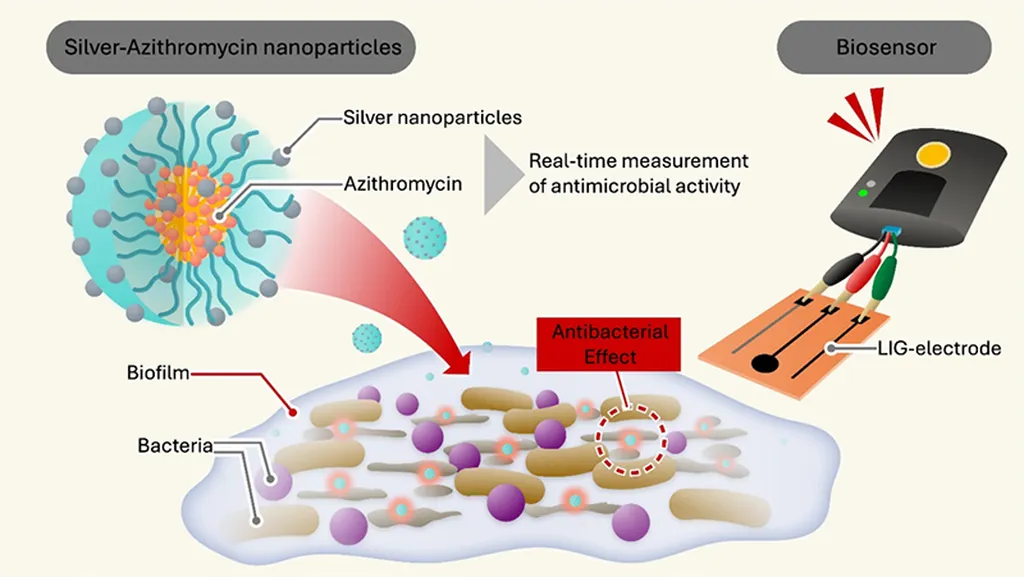
In the relentless battle against multidrug-resistant bacteria, a new ally has emerged from the realm of nanotechnology. Antimicrobial nanoparticles (NPs) are stepping into the spotlight, offering a promising frontier in the fight against infections that have become increasingly resistant to conventional antibiotics. A recent review published in *Frontiers in Nanotechnology* delves into the mechanisms, applications, and future prospects of these tiny yet powerful warriors, with significant implications for the agriculture sector.
Antimicrobial nanoparticles leverage their unique physicochemical properties to combat bacterial infections through multiple mechanisms. These include generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), disrupting cell membranes, damaging DNA and proteins, and interfering with metabolic pathways and the electron transport chain. “The broad-spectrum efficacy of antimicrobial NPs, coupled with a lower risk of resistance, makes them a compelling alternative to traditional antibiotics,” says Ambika Chaturvedi, lead author of the study and a researcher at the Plant Molecular Biology Lab, Department of Botany, Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Agra, India.
The applications of antibacterial NPs are vast and varied, spanning food safety, water purification, healthcare, and agriculture. In the agricultural sector, these nanoparticles hold particular promise for disease management and plant protection. Imagine crops shielded from pathogens by nanotechnology-enhanced coatings, or antimicrobial packaging that extends the shelf life of produce while ensuring food safety. These innovations could revolutionize the way we approach plant health and food preservation, potentially reducing crop losses and enhancing food security.
However, the path to widespread adoption is not without challenges. Concerns about toxicity, environmental impact, and regulatory limitations must be addressed to ensure the sustainable use of antimicrobial nanoparticles. “While the potential is immense, we must proceed with caution,” Chaturvedi emphasizes. “Understanding the long-term effects and developing robust regulatory frameworks will be crucial for harnessing the full benefits of antimicrobial NPs.”
The study highlights the need for further research to optimize the use of these nanoparticles, ensuring their safety and efficacy across various applications. As we stand on the brink of a nanotechnology revolution in agriculture, the insights from this review could shape the future of plant protection and food safety, offering new tools to combat the persistent threat of multidrug-resistant bacteria.
In the evolving landscape of agricultural technology, antimicrobial nanoparticles represent a beacon of hope, promising innovative solutions to some of the sector’s most pressing challenges. As research continues to unfold, the agricultural industry stands to gain significantly from these nanoscale guardians, paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable future.