In the ever-evolving landscape of modern agriculture, precision and predictability are key to maximizing yields and economic returns. A recent study published in the ‘BIO Web of Conferences’ is making waves by introducing a novel approach to analyzing perennial plantations using neural networks. Led by Dzhumabaev Alymkul from the Institute of Economics at the National Academy of Sciences, this research promises to revolutionize how farmers and agribusinesses plan and manage their operations.
The study addresses a critical need in the agricultural sector: the ability to accurately forecast yields and economic outcomes despite the inherent uncertainties and complex interactions between various agrobiological and economic parameters. Traditional methods, while useful, often fall short in capturing the intricate relationships that influence perennial crops.
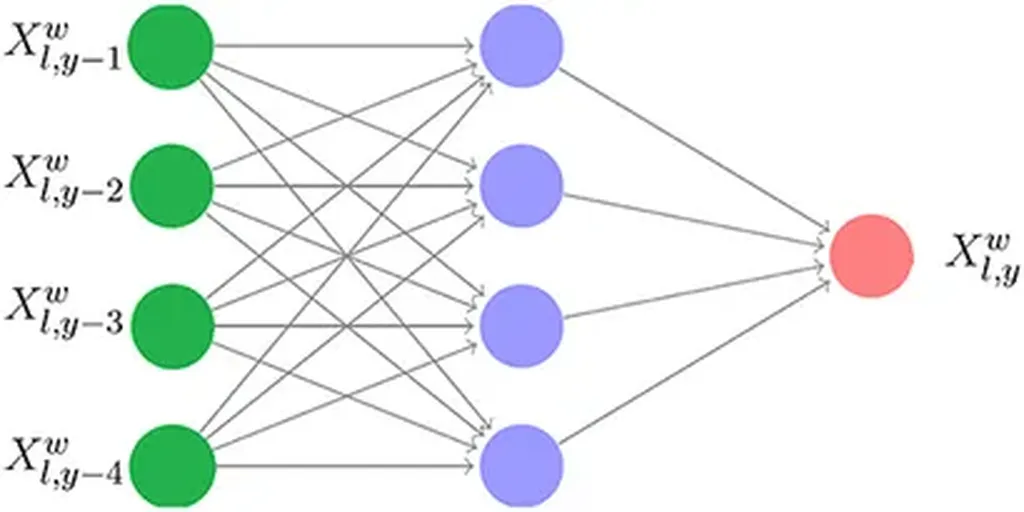
Dzhumabaev and his team developed a deep learning model that integrates biophysical, climatic, and production-economic parameters. The model was trained on multi-year data encompassing yields, meteorological conditions, and financial results from various farms. The results were striking. Neural network forecasting outperformed traditional economic and mathematical methods by a significant margin, increasing the accuracy of yield forecasts by 20% and the reliability of economic evaluations by 15%.
“This improvement in accuracy and reliability can have profound implications for the agricultural sector,” Dzhumabaev explained. “Farmers and agribusinesses can make more informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately enhance their economic returns.”
The practical significance of this research is immense. By integrating neural network algorithms into decision support systems, farmers can better plan their planting and harvesting schedules, manage resources more efficiently, and mitigate risks associated with unpredictable weather patterns and market fluctuations. This could lead to more sustainable and profitable agricultural practices, benefiting both individual farmers and the broader economy.
The study also lays the groundwork for further advancements in digital farming methods. As Dzhumabaev noted, “The integration of neural networks into agricultural management systems is just the beginning. Future research could explore the use of more sophisticated models and larger datasets to further refine predictions and decision-making processes.”
The commercial impacts of this research are far-reaching. For agribusinesses, the ability to predict yields and economic outcomes with greater accuracy can lead to better investment decisions, improved supply chain management, and enhanced market competitiveness. For policymakers, the insights gained from this research can inform strategies aimed at promoting sustainable agriculture and food security.
As the agricultural sector continues to embrace digital transformation, the integration of neural networks into decision support systems represents a significant step forward. The research led by Dzhumabaev Alymkul from the Institute of Economics at the National Academy of Sciences, published in the ‘BIO Web of Conferences’, highlights the potential of advanced technologies to address longstanding challenges in the field. By leveraging the power of neural networks, farmers and agribusinesses can look forward to a future of increased efficiency, sustainability, and profitability.