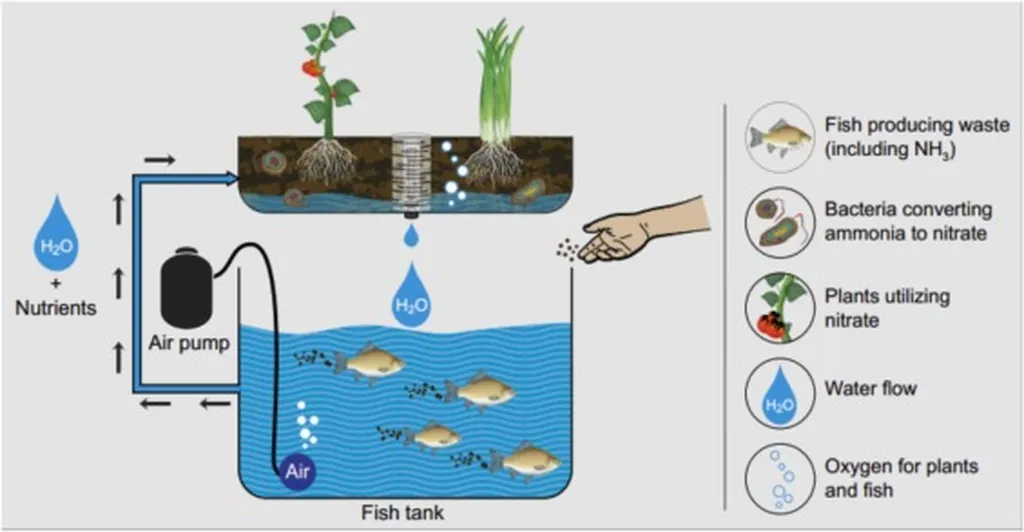
In the rapidly evolving world of smart agriculture, a groundbreaking study has emerged that could redefine how we approach aquaponic farming. Researchers have successfully integrated multi-modal sensors with an aquaponic farming platform, leveraging the combined power of Raspberry Pi and ESP32 microcontrollers. This innovative approach promises to enhance data acquisition, processing, and control, potentially revolutionizing the agriculture sector.
The study, led by Muhammad Risal from Universitas Handayani Makassar, focuses on creating a robust smart agriculture system. By integrating various sensors, the system can gather comprehensive environmental and operational data from aquaponic systems. This data is then processed and transmitted using the ESP32 and Raspberry Pi platforms, which work in tandem to ensure accurate and reliable performance.
“Our research demonstrates that the integration of Raspberry Pi and ESP32 platforms offers superior performance compared to using a single platform,” Risal explains. “The ESP32 excels at reading analog sensor data and transmitting it to the Raspberry Pi, which then functions as the central data processing unit. This synergy enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of the system.”
The implications for the agriculture sector are profound. Aquaponic farming, which combines aquaculture and hydroponics, is already known for its sustainability and efficiency. By incorporating multi-modal sensors and IoT technology, farmers can gain real-time insights into their systems, enabling them to make data-driven decisions. This can lead to improved crop yields, optimized resource usage, and reduced operational costs.
“The integration of IoT technology with aquaponic farming is a game-changer,” says Risal. “It allows for precise monitoring and control of environmental factors, ensuring optimal growing conditions for both plants and fish. This not only enhances productivity but also promotes sustainable farming practices.”
The study, published in the ‘Journal of Applied Informatics and Computing’, highlights the potential for future implementations of IoT-based control systems in agriculture. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see more innovative solutions that enhance the efficiency and sustainability of farming practices.
This research is a significant step forward in the field of smart agriculture. By integrating multi-modal sensors with aquaponic farming platforms, researchers have demonstrated the potential to transform the way we grow food. As the technology becomes more widely adopted, it could pave the way for a more sustainable and efficient future in agriculture.