In the heart of India’s agricultural landscape, a technological revolution is brewing, promising to reshape the way farmers approach crop cultivation and fertilizer application. Researchers have developed a sophisticated deep learning model that offers independent, data-driven recommendations for both crops and fertilizers, potentially transforming the agriculture sector’s approach to resource efficiency and productivity.
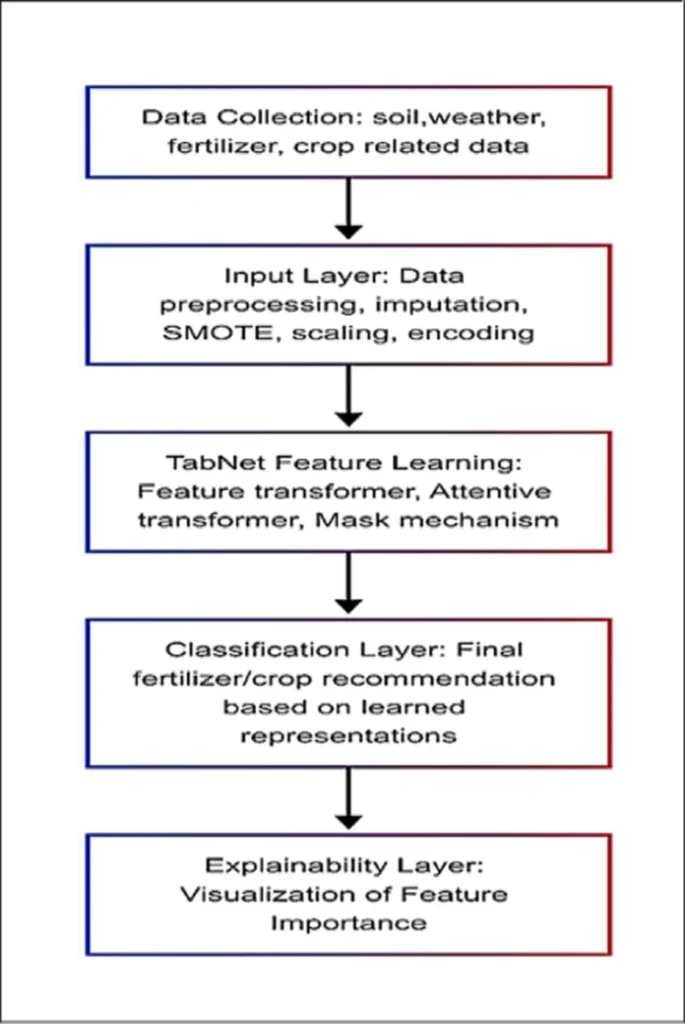
The study, published in *Scientific Reports*, leverages the power of TabNet, a deep learning architecture tailored for tabular data, to analyze IoT-enabled agricultural data. This innovative approach enables the model to identify crucial patterns without the need for prior feature selection, a common stumbling block in traditional machine learning methods. “Our model directly discovers important patterns from preprocessed IoT-enabled agricultural data,” explains Stella Mary Venkateswara, lead author of the study and a researcher at the Department of Computer Technology, MIT, Anna University. “This allows for accurate and interpretable crop and fertilizer classifications.”
The implications for the agriculture sector are substantial. By maximizing yield and promoting resource efficiency, this technology can help farmers reduce costs and minimize environmental impact. Traditional farming practices often lead to nutrient inefficiency and soil health degradation, negatively impacting productivity. This new approach aims to mitigate these issues by providing tailored recommendations based on real-time data.
The model’s performance is impressive, achieving classification accuracies of 95.24% for fertilizer recommendations and 96.21% for crop recommendations. These results outperform conventional classifiers and existing approaches, demonstrating the potential for widespread adoption in the agriculture industry.
The study employed robust preprocessing techniques, such as iterative imputation and the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE), to ensure data quality and class balance. The model’s performance and generalizability were rigorously assessed using fivefold cross-validation, maintaining high accuracy levels across folds.
Beyond its immediate applications, this research could pave the way for future developments in smart farming. The integration of AI and IoT technologies is fundamentally transforming agriculture, enabling real-time data collection and analysis. As these technologies continue to evolve, they hold the promise of even greater efficiencies and innovations in the field.
“This is just the beginning,” Venkateswara notes. “As we continue to refine and expand these models, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and effective solutions for the challenges facing modern agriculture.”
For the agriculture sector, the potential commercial impacts are significant. By optimizing resource use and enhancing productivity, this technology can help farmers stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world. As the industry continues to embrace digital transformation, innovations like this will be crucial in shaping the future of farming.