In the ever-evolving landscape of precision agriculture, a groundbreaking development has emerged from the Smart Agriculture Research Institute at Jilin Agricultural University in China. Researchers, led by Zhenyang Chen, have introduced a deep learning framework that promises to revolutionize the classification of Japonica rice varieties. This innovation, detailed in a recent study published in *Industrial Crops and Products*, could significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of rice breeding, quality assessment, and market grading, with profound implications for the agriculture sector.
Japonica rice, a staple crop cherished for its quality and versatility, exhibits substantial variations across different varieties. These differences can impact yield, economic viability, and food processing outcomes. Traditional classification methods, however, often fall short in terms of precision and efficiency. Enter J-Rice-ResNeXt, a deep learning model designed to address these challenges head-on.
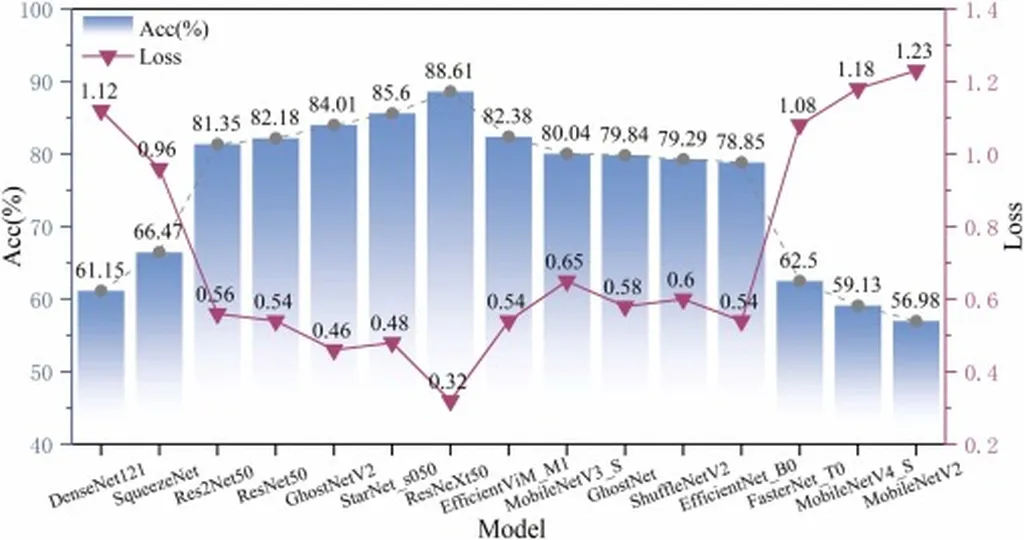
The research team constructed a dataset by collecting 200 seeds from each of nine Japonica rice varieties, totaling 1,800 seeds. They employed image segmentation and data augmentation techniques to build a robust dataset. During the pre-training phase, fifteen established deep learning models were evaluated, with the ResNeXt50 model emerging as the top performer. The researchers then refined the ResNeXt50 model by substituting the activation function, convolution operation, downsampling method, and integrating the ECA attention mechanism, resulting in the J-Rice-ResNeXt network model.
The proposed J-Rice-ResNeXt model achieved an impressive accuracy rate of 98.81%, a 7.82% improvement over the original ResNeXt50 model. Moreover, it reduced the parameter count and computational demand by 10.279 million and 1.573 gigabytes, respectively. The model also demonstrated faster convergence and superior fitting capabilities.
“This advancement is a game-changer for the agriculture sector,” said Zhenyang Chen, lead author of the study. “By accurately classifying Japonica rice varieties, we can enhance breeding programs, ensure quality assessment, and streamline market grading processes. This not only improves economic outcomes but also supports the broader goals of agricultural intelligence and precision farming.”
The implications of this research are vast. For rice breeders, the ability to accurately classify varieties can lead to more targeted breeding programs, improving yield and quality. For quality assessors, the model provides a reliable tool to ensure consistency and meet market standards. For market graders, the efficiency and accuracy of the classification process can streamline operations and reduce costs.
As the agriculture sector continues to embrace digital transformation, innovations like J-Rice-ResNeXt are poised to play a pivotal role. The model’s ability to handle large datasets and deliver high accuracy makes it a valuable asset for future developments in agricultural intelligence. By integrating such advanced technologies, the sector can achieve greater precision, efficiency, and sustainability.
The study, published in *Industrial Crops and Products*, represents a significant step forward in the application of deep learning in agriculture. As the research team continues to refine and expand the model’s capabilities, the potential for transforming the agriculture sector becomes increasingly evident. This research not only highlights the power of deep learning but also underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in driving agricultural innovation.
In the words of Zhenyang Chen, “The future of agriculture lies in the integration of advanced technologies. Our work is just the beginning, and we are excited about the possibilities that lie ahead.” With the J-Rice-ResNeXt model leading the way, the agriculture sector is poised to enter a new era of precision and efficiency, driven by the power of deep learning.