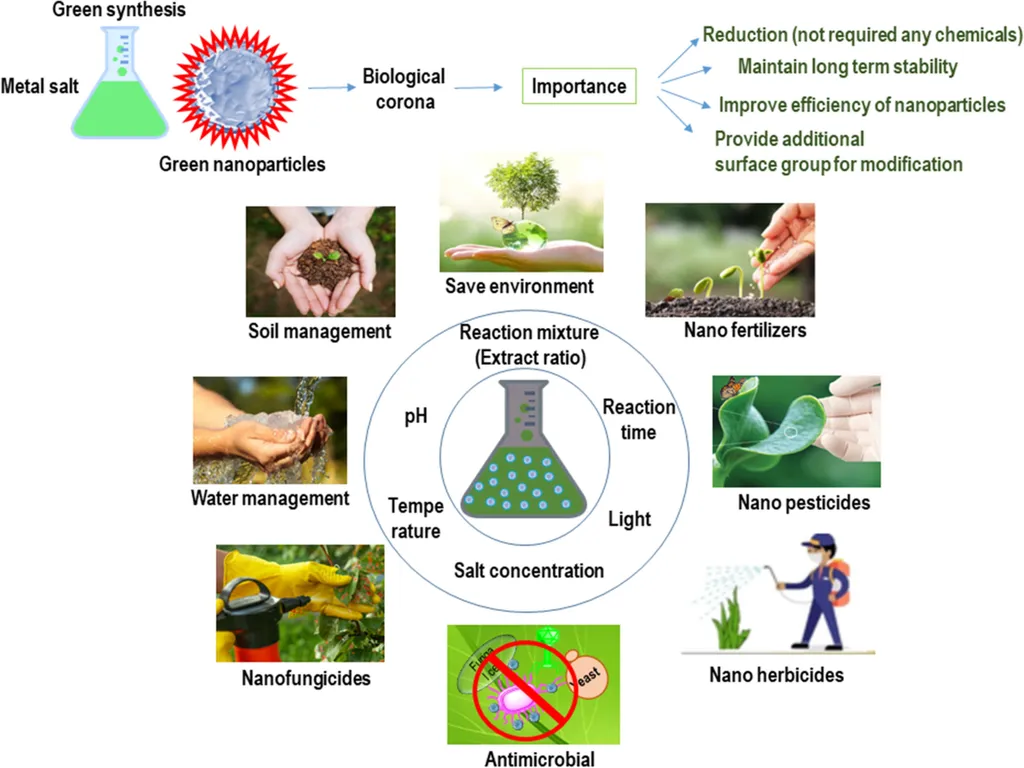
In the quest for sustainable agriculture, scientists are turning to an unlikely ally: bacteria. A recent perspective article published in *Frontiers in Microbiology* explores how biogenic nanoparticles (BNPs) synthesized by bacteria could revolutionize agricultural practices, offering a green alternative to conventional methods. The research, led by Natalia Bilesky-Jose of the Laboratory for Evaluation of the Bioactivity and Toxicology of Nanomaterials at the University of Sorocaba (UNISO), Brazil, delves into the potential of these nanoparticles to enhance crop productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
BNPs are nanomaterials produced by bacteria through a process known as biogenic synthesis. Unlike chemically synthesized nanoparticles, BNPs are environmentally friendly, making them an attractive option for sustainable agriculture. The perspective article highlights the mechanistic basis of bacterial nanoparticle biosynthesis and discusses strategies for genetic and metabolic optimization to improve yield and functionality.
One of the most promising applications of BNPs in agriculture is their use as phytosanitary agents and controlled-release fertilizers. “Biogenic nanoparticles can be engineered to deliver nutrients directly to plants, reducing waste and increasing efficiency,” explains Bilesky-Jose. This targeted approach not only boosts crop yields but also minimizes the environmental footprint of agricultural practices.
The article proposes an integrative “BNP–Plant–Microbiome” framework, where microbial consortia and multi-nanoparticle formulations work synergistically to deliver nutrients, enhance stress resilience, and suppress pathogens. This holistic approach could transform how farmers manage their crops, leading to more sustainable and productive agricultural systems.
However, the path to widespread adoption of BNPs in agriculture is not without challenges. Issues such as biosafety, regulatory compliance, and large-scale bioprocessing need to be addressed. Additionally, integrating BNPs with precision agriculture and data-driven monitoring tools will be crucial for maximizing their potential.
The commercial implications of this research are significant. As the global demand for sustainable agricultural solutions grows, BNPs could become a key player in the market. Farmers and agribusinesses stand to benefit from the increased efficiency and reduced environmental impact offered by these innovative nanomaterials.
Looking ahead, the research suggests that bacterial BNPs have the potential to redefine agricultural sustainability. By coupling microbial innovation with circular, resource-efficient crop management systems, BNPs could pave the way for a more sustainable future in agriculture.
As the scientific community continues to explore the applications of BNPs, the findings presented in this perspective article offer a glimpse into the transformative potential of these nanomaterials. With further research and development, bacterial BNPs could become a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, benefiting farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.