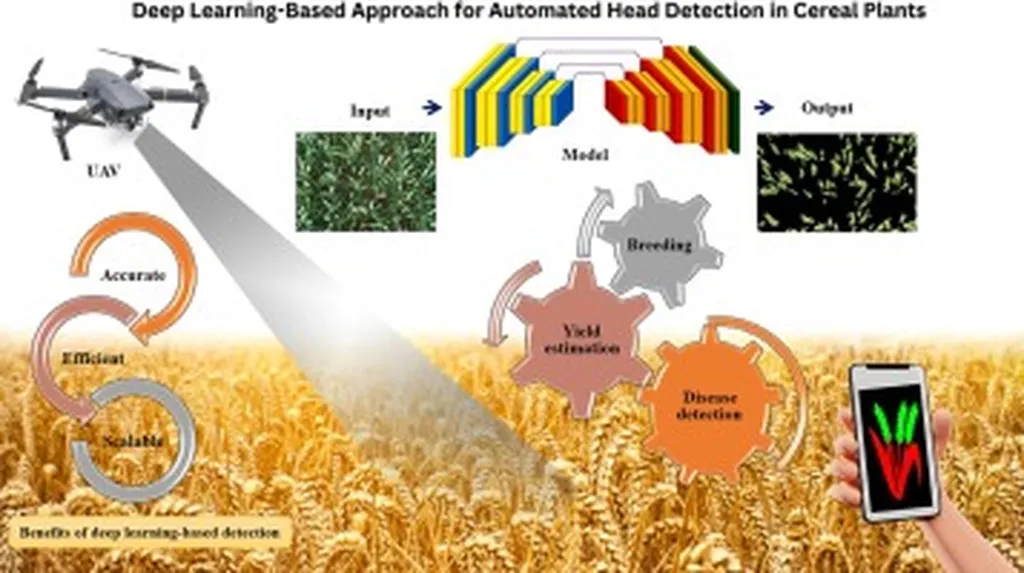
In the rapidly evolving world of precision agriculture, deep learning is proving to be a game-changer, particularly in the realm of remote sensing image segmentation. A recent review published in the *Journal of Agricultural Engineering* sheds light on how these advanced techniques are transforming the way we analyze agricultural data, with significant implications for the industry.
Remote sensing image segmentation, the process of classifying each pixel of an image into specific categories, has traditionally been a challenging task. However, the advent of deep learning methods has revolutionized this field due to their superior feature extraction capabilities. Qinghua Ren, lead author of the review and a researcher at the School of Computer Science and Communication Engineering, Jiangsu University, explains, “Deep learning models have shown remarkable potential in accurately segmenting agricultural remote sensing images, which is crucial for various applications such as crop monitoring, yield estimation, and pest detection.”
The review systematically outlines the evolution of deep learning-based segmentation techniques, highlighting various network architectures such as convolution-based models, transformer-based models, and hybrid architectures. These advancements have enabled more precise and efficient analysis of agricultural data, which can lead to better decision-making and improved productivity.
One of the key challenges addressed in the review is the need for annotation-efficient scenarios. Deep learning paradigms such as semi-supervised, weakly supervised, self-supervised, and transfer learning are discussed as potential solutions. These methods can significantly reduce the need for large annotated datasets, making the technology more accessible and cost-effective for farmers and agricultural businesses.
The commercial impacts of these advancements are substantial. Accurate and timely analysis of remote sensing images can help farmers optimize resource use, reduce costs, and increase yields. For instance, precise crop monitoring can enable early detection of diseases or pests, allowing for targeted interventions that minimize crop loss. Similarly, yield estimation can help in planning and logistics, ensuring that the produce reaches the market at the right time and in the right quantities.
Moreover, the review highlights the potential for these technologies to be integrated into existing agricultural systems, making them more robust and adaptable. As Qinghua Ren notes, “The integration of deep learning in agricultural remote sensing is not just about improving accuracy; it’s about creating a more resilient and sustainable agricultural ecosystem.”
Looking ahead, the review outlines several future research directions, including the development of more efficient and lightweight models, improving model generalization, and addressing computational costs. These advancements could further enhance the practical application of deep learning in agriculture, making it an indispensable tool for the industry.
In conclusion, the review by Qinghua Ren and colleagues provides a comprehensive overview of the current state and future potential of deep learning-based agricultural remote sensing image segmentation. As the technology continues to evolve, it is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of agriculture, driving innovation and sustainability in the sector.