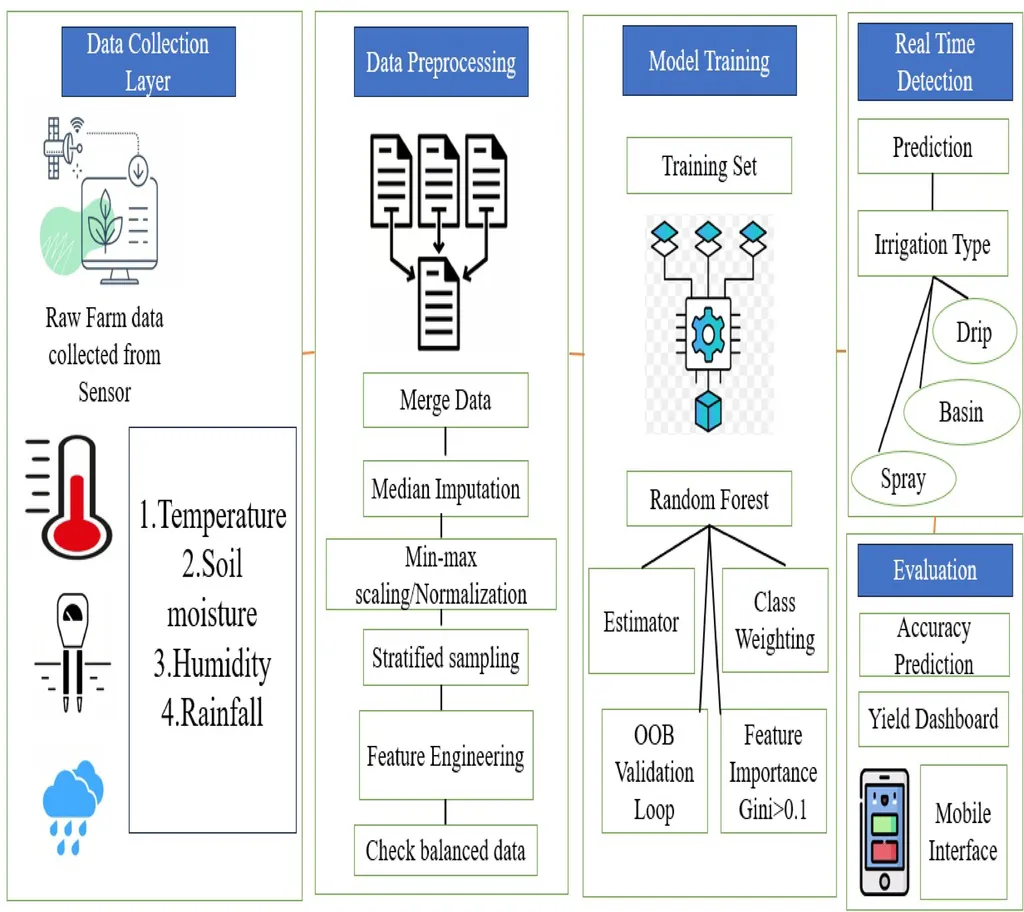
In an era where climate change is reshaping our world, the ability to predict extreme weather events has become more critical than ever. A groundbreaking study published in *Discover Internet of Things* introduces a novel framework that could revolutionize how we anticipate and respond to extreme temperatures, with significant implications for agriculture and other sectors.
The Geo-Blockchain Intelligence Risk Assessment (GBIRA) framework, developed by lead author Hana M. Saraya of the Information Systems Department at Mansoura University, integrates blockchain, artificial intelligence, risk assessment, spatial big data, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to create a robust climate intelligence prediction model. This innovative approach aims to tackle the challenges posed by the vast amounts of geospatial data generated daily, which often overwhelm existing algorithms.
“Predicting extreme temperatures is a complex task due to the intricate interplay of various climate variables,” explains Saraya. “Our framework seeks to simplify this process by leveraging advanced technologies to assess risks and their impacts on critical assets, ultimately supporting better decision-making in climate-related scenarios.”
For the agriculture sector, the implications are profound. Farmers and agribusinesses often face significant losses due to unpredictable weather patterns. The GBIRA framework could provide more accurate and timely predictions, enabling farmers to make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and resource management. This could lead to increased crop yields, reduced waste, and improved overall efficiency in agricultural operations.
Moreover, the framework introduces GBIRA-as-a-Service, a novel computing paradigm that enhances environmental-human interaction through advanced theoretical and scientific methods. This service could be particularly valuable for smart cities, emergency response systems, and other sectors that rely on precise weather forecasting.
The integration of blockchain technology ensures data integrity and interoperability, while homomorphic encryption allows for privacy-preserving collaborative weather forecasting across organizational boundaries. This means that sensitive data can be shared and analyzed without compromising privacy, a crucial aspect for industries dealing with large-scale data.
As we look to the future, the GBIRA framework could shape the development of more sophisticated climate prediction models. By providing a secure, scalable solution for real-time extreme weather prediction, it sets a new standard for environmental monitoring and disaster risk management. The research not only contributes to academic knowledge but also offers practical applications that can drive innovation and resilience in the face of climate change.
In the words of Saraya, “This framework is a step towards creating a more sustainable and resilient future, where technology plays a pivotal role in mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events.” As we continue to grapple with the challenges posed by climate change, such advancements in technology and data analysis will be invaluable in our collective efforts to adapt and thrive.