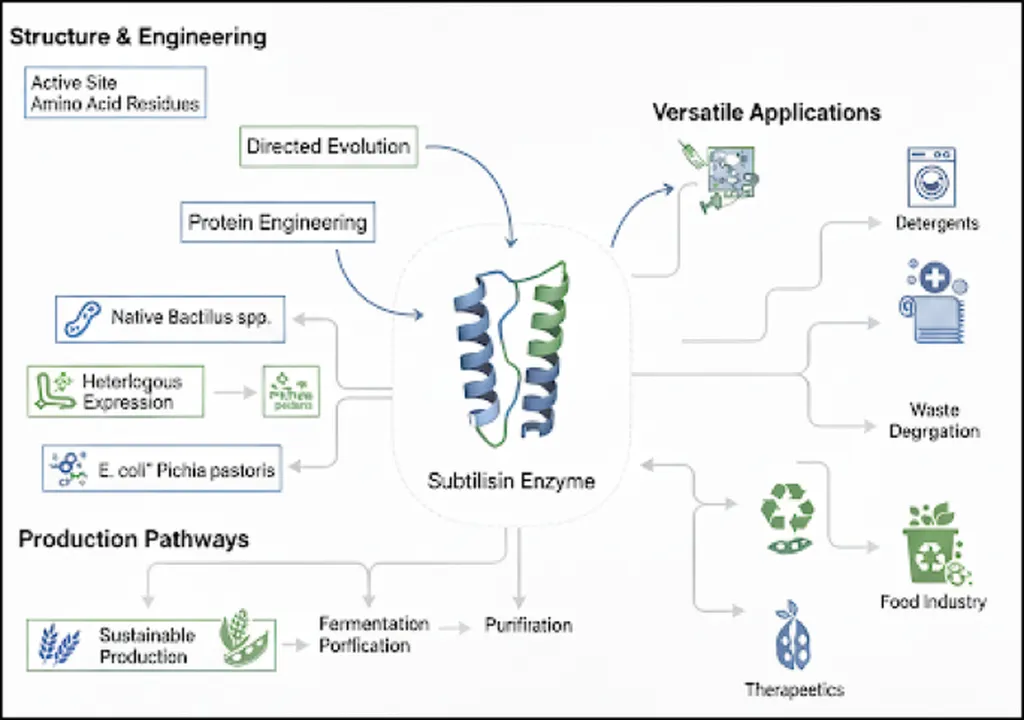
In the ever-evolving landscape of biotechnology, subtilisin, a versatile enzyme, continues to captivate researchers worldwide. A recent comprehensive review published in *Discover Applied Sciences* sheds light on the latest advancements in subtilisin research, highlighting its structural intricacies, sustainable production methods, and diverse applications. The review, led by Shreya S. Shettar from the Department of Biotechnology at KLE Technological University, integrates bibliometric data and cutting-edge scientific insights to provide a forward-looking perspective on this enzyme’s potential.
The bibliometric analysis reveals a significant global interest in subtilisin research, with Saudi Arabia and South Korea emerging as leaders in publication productivity per million people (PPMP). This surge in research activity underscores the enzyme’s adaptability and broad applications, ranging from industrial processes to therapeutic developments.
One of the most compelling aspects of the review is its focus on sustainable production methods. By utilizing agricultural waste, researchers have found a way to reduce production costs by up to 60%, promoting a circular economy that benefits both the environment and the agriculture sector. “This shift towards sustainable production not only cuts costs but also aligns with global efforts to reduce waste and promote eco-friendly practices,” notes Shettar.
The review also delves into recent advancements in structural and computational biology, which have provided a deeper understanding of subtilisin’s activity and stability. This knowledge paves the way for targeted engineering, enabling the creation of enzyme variants tailored to specific industrial needs. “Understanding the enzyme’s structure at a molecular level allows us to engineer subtilisin for enhanced performance in various applications,” explains Shettar.
Subtilisin’s applications are vast and varied. In the textile industry, it is used for biopolishing, improving fabric quality and durability. In waste management, it aids in the breakdown of organic waste, contributing to more efficient waste treatment processes. Therapeutically, subtilisin shows promise in wound healing and thrombolysis, offering new avenues for medical research and development.
Looking ahead, the review identifies several opportunities for future research. Synthetic biology holds the potential for creating tailor-made subtilisin variants, while AI-driven enzyme design could accelerate the engineering process. “The future of subtilisin research lies in harnessing these advanced technologies to develop enzymes with enhanced properties and broader applications,” says Shettar.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Optimizing subtilisin’s performance under harsh industrial conditions is an ongoing endeavor. However, the review underscores the enzyme’s biotechnological potential and its role in bridging foundational research with industrial innovation.
As the agriculture sector continues to seek sustainable and cost-effective solutions, subtilisin’s versatile applications offer a promising avenue for growth and development. The insights provided by this review could shape future developments in the field, driving innovation and promoting a more sustainable future.
For those interested in the intricacies of subtilisin research, the comprehensive review by Shreya S. Shettar and her team, published in *Discover Applied Sciences*, offers a wealth of information and a forward-looking perspective on this versatile enzyme’s potential.