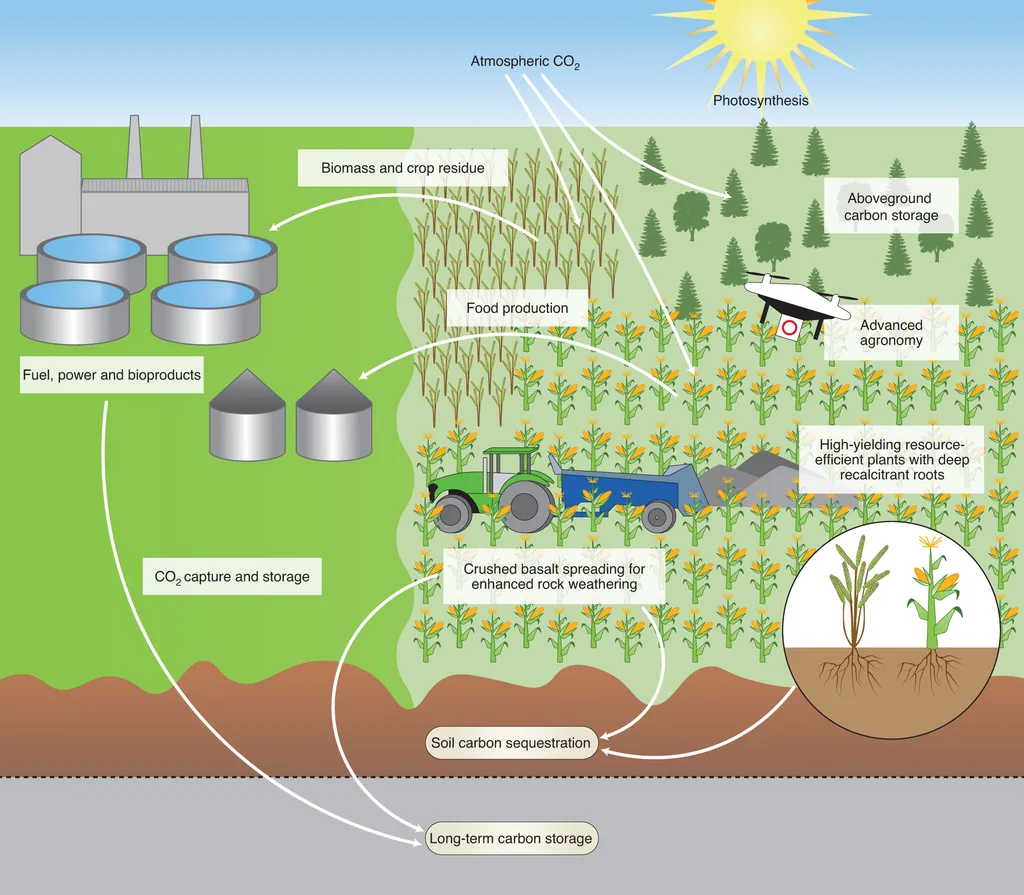
In a world grappling with the dual challenges of climate change and food security, a new review published in *Energy Science & Engineering* offers a beacon of hope for the agriculture sector. The study, led by Ravikumar Jayabal from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at AMET University in Chennai, India, underscores the urgent need for low-carbon agricultural strategies and the integration of cutting-edge technologies to mitigate environmental degradation and enhance energy efficiency.
Traditional agricultural practices have long been criticized for their significant contributions to soil degradation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. These practices, while historically effective in feeding populations, are increasingly unsustainable in the face of climate change and growing environmental awareness. Jayabal’s review synthesizes a wealth of research to highlight the potential of precision agriculture, the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data analytics, and renewable energy applications in transforming the agricultural landscape.
“Transitioning from conventional farming systems to sustainable models is not just an environmental imperative but also a commercial opportunity,” Jayabal asserts. The review indicates that low-carbon strategies can substantially reduce the carbon footprint of agricultural systems, minimize soil erosion, decrease water pollution, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. These benefits are not merely environmental; they also translate into significant economic advantages. By optimizing resource use and energy efficiency, farmers can reduce operational costs and enhance productivity, making agriculture more resilient and profitable in the long run.
The integration of precision agriculture, which uses advanced technologies to monitor and manage field conditions, allows for more targeted and efficient use of inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. This precision not only reduces waste but also improves crop yields and quality. Similarly, the IoT enables real-time data collection and analysis, providing farmers with actionable insights to make informed decisions. AI and Big Data analytics further enhance this capability by predicting trends and optimizing resource allocation.
Renewable energy applications, such as solar-powered irrigation systems and biogas production from agricultural waste, offer additional avenues for reducing the sector’s carbon footprint. These technologies not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also create new revenue streams for farmers. For instance, selling excess renewable energy back to the grid can provide a supplementary income, diversifying farmers’ earnings and enhancing their financial stability.
The commercial impacts of these low-carbon strategies are profound. As consumer demand for sustainably produced food continues to grow, farmers who adopt these practices can tap into premium markets and command higher prices for their products. Additionally, governments and international organizations are increasingly offering incentives and subsidies for sustainable farming practices, further incentivizing the transition to low-carbon agriculture.
Looking ahead, the integration of these technologies and strategies is poised to reshape the agricultural sector. “The future of agriculture lies in its ability to adapt and innovate,” Jayabal notes. By embracing low-carbon strategies and smart technologies, the sector can become more adaptable, environmentally responsible, and economically viable. This transition is not just about mitigating environmental damage; it is about building a more sustainable and resilient food system that can meet the demands of a growing global population.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change and food security, the insights from Jayabal’s review offer a roadmap for the future of agriculture. By leveraging advanced technologies and sustainable practices, the sector can achieve a delicate balance between environmental protection and economic prosperity, ensuring a secure and sustainable future for generations to come.