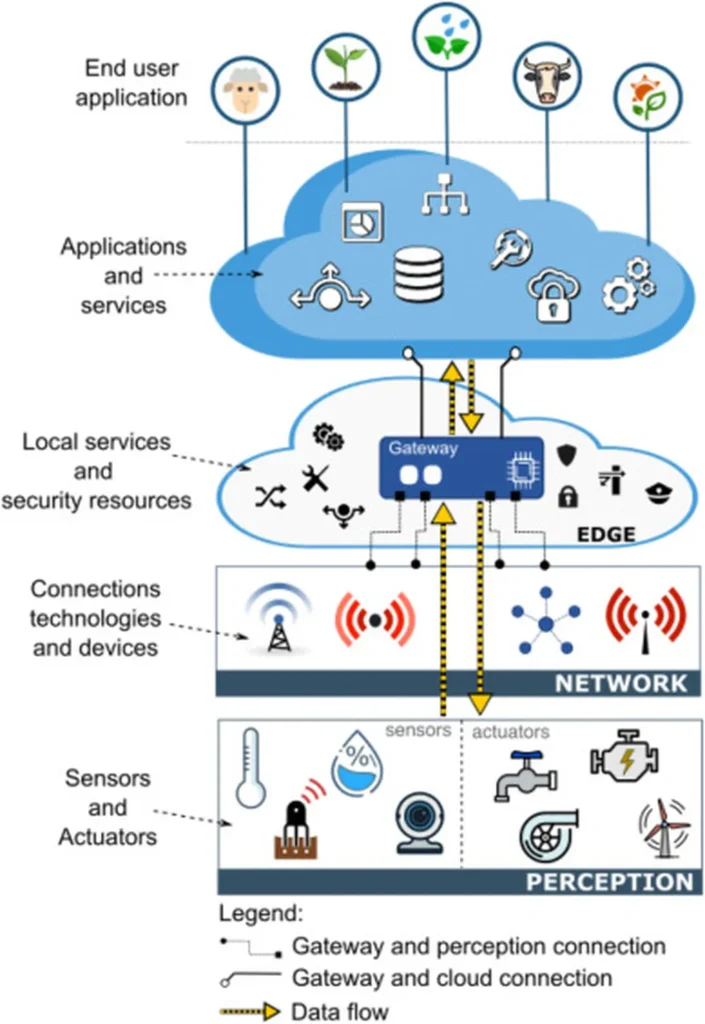
In the rapidly expanding world of Internet of Things (IoT) applications, LoRaWAN technology has emerged as a cornerstone for long-range, low-power communication. However, as its adoption grows—particularly in sectors like agriculture, where it enables efficient monitoring of crops, soil, and livestock—so do concerns about its security vulnerabilities. A recent comprehensive survey published in *IEEE Access* sheds light on these challenges, offering a detailed analysis of the threats LoRaWAN systems face across multiple layers of their architecture.
The study, led by Josemaria Chukwuemeka Osuorah of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Prairie View A&M University, categorizes vulnerabilities into physical, MAC (Medium Access Control), and application layers. These include jamming, eavesdropping, replay attacks, key reuse, and packet injection—each posing significant risks to the integrity and reliability of LoRaWAN networks. “The lightweight design of LoRa, while advantageous for constrained environments, introduces critical security gaps that adversaries can exploit,” Osuorah explains. “Understanding these vulnerabilities is the first step toward building more resilient systems.”
For the agriculture sector, where LoRaWAN is increasingly used to monitor environmental conditions, manage irrigation, and track livestock, these security concerns are particularly pressing. A compromised network could lead to disrupted operations, data breaches, or even financial losses. For instance, an attacker injecting false data into a soil moisture monitoring system could mislead farmers into over- or under-watering their crops, impacting yields and profitability.
The survey also highlights the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques to detect intrusions and anomalies in LoRa-based systems. By leveraging these technologies, farmers and agricultural businesses could proactively identify and mitigate threats, ensuring the security and reliability of their IoT deployments.
As the agriculture sector continues to embrace IoT technologies, the findings of this survey serve as a crucial guide for developers, engineers, and policymakers. By addressing the vulnerabilities outlined in the study, stakeholders can design more secure and resilient LoRaWAN networks, safeguarding the future of smart agriculture. “This research not only identifies the weaknesses in current systems but also points toward innovative solutions that could shape the future of IoT security,” Osuorah notes.
The survey, published in *IEEE Access*, provides a structured reference for designing secure LoRa networks and guides future research directions. As the agriculture sector increasingly relies on IoT technologies, understanding and mitigating these vulnerabilities will be essential for ensuring the security and efficiency of smart farming practices.