In the heart of India’s agricultural landscape, a new breakthrough is set to revolutionize how farmers detect and manage jackfruit leaf diseases. Researchers have developed an advanced deep-learning model called CNNAttLSTM, which promises to transform plant disease detection with its high precision and efficiency. This innovation could significantly impact the agricultural sector, particularly in regions where jackfruit cultivation is prevalent.
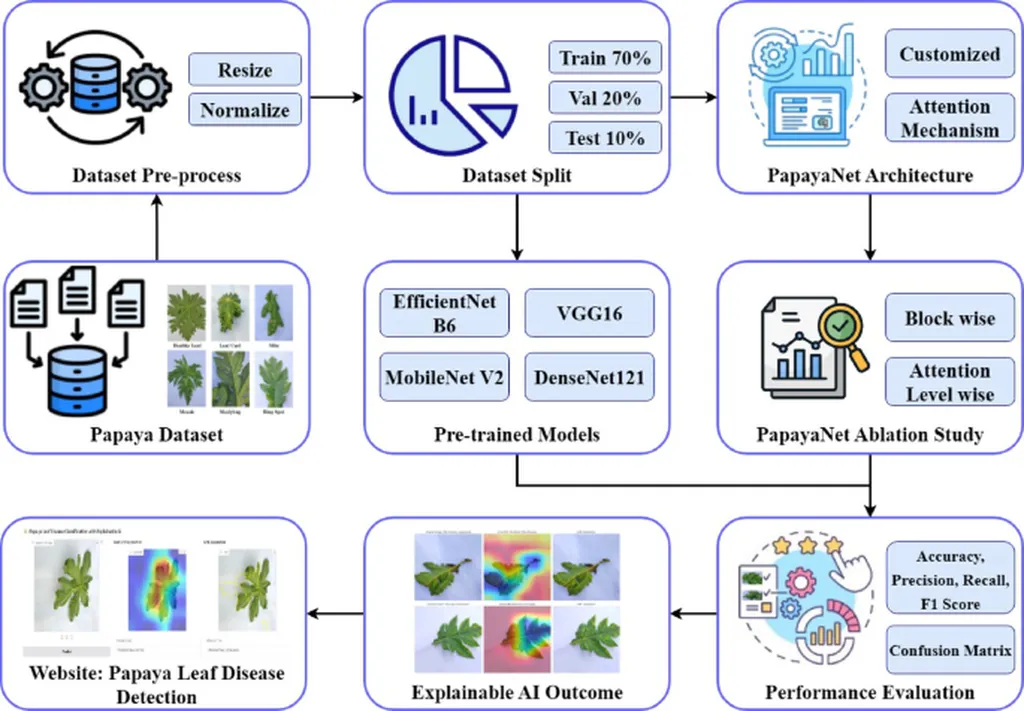
The CNNAttLSTM model, detailed in a recent study published in *Frontiers in Plant Science*, combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) units, and an attention mechanism to classify jackfruit leaf diseases with remarkable accuracy. The model’s unique approach involves dividing each leaf image into ordered spatial patches, treating them as pseudo-temporal sequences to capture contextual dependencies across different leaf regions.
“Our model achieves 99% classification accuracy, which is a significant improvement over existing methods,” said Gaurav Tuteja, the lead author of the study from Chitkara University Institute of Engineering and Technology, Chitkara University, Punjab, India. “This level of precision is crucial for early disease detection, which can prevent yield losses and improve fruit quality.”
The implications for the agricultural sector are substantial. Jackfruit cultivation is highly susceptible to diseases like algal leaf spot and black spot, which can reduce yield and negatively impact farmer income. Traditional manual inspection methods are often time-consuming and prone to human error. The CNNAttLSTM model offers a scalable and automated solution that can be deployed in real-time, even on edge devices, making it accessible for farmers in various settings.
The model’s efficiency is another key advantage. It requires only 3.7 million parameters and can be trained in just 45 minutes on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU, with an inference time of 22 milliseconds per image. This computational efficiency makes it feasible for widespread adoption, addressing a major limitation of existing deep-learning techniques.
The study’s findings highlight the potential of combining spatial feature extraction with temporal modeling and attention mechanisms to enhance robustness and classification performance. This approach could pave the way for more advanced and efficient agricultural disease monitoring systems, contributing to the broader field of precision agriculture.
As the agricultural sector continues to embrace technological advancements, the CNNAttLSTM model represents a significant step forward in the fight against plant diseases. Its high precision, efficiency, and scalability make it a valuable tool for farmers and agricultural professionals, ultimately contributing to increased productivity and sustainability in the sector.