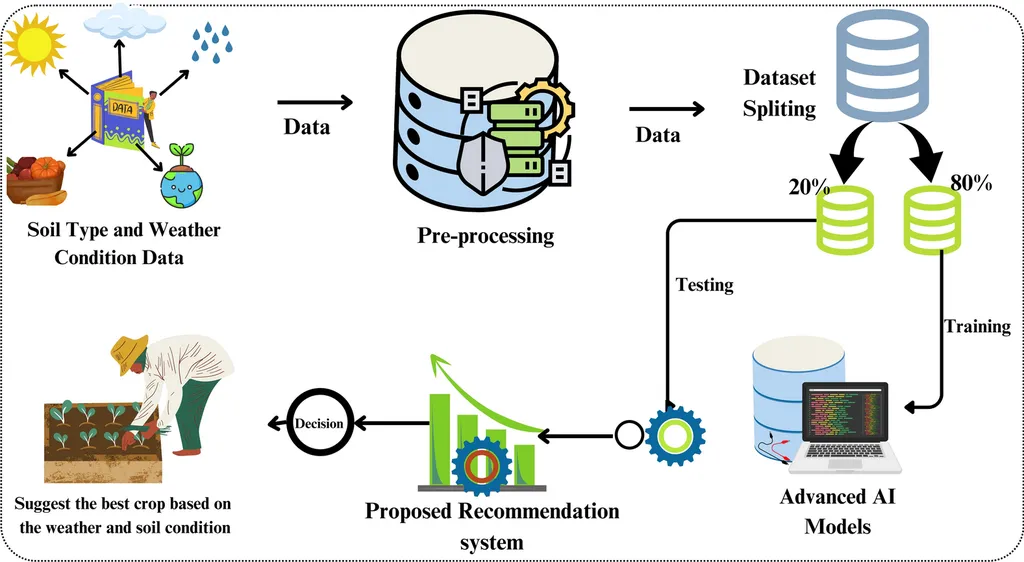
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern agriculture, data-driven decision-making is becoming increasingly vital for farmers aiming to maximize yields and optimize resource use. A recent study published in *Computer Science* sheds light on the potential of ensemble learning techniques to revolutionize crop recommendation systems, offering a promising path toward more sustainable and productive farming practices.
The research, led by Siti Marlina of Universitas Bina Sarana Informatika, evaluated the performance of five ensemble learning algorithms—Random Forest, Extra Trees, CatBoost, XGBoost, and LightGBM—in a multiclass classification framework for crop recommendation. All models achieved impressive accuracy rates above 98%, with Random Forest emerging as the top performer. “The stability and accuracy of Random Forest make it a robust choice for farmers seeking reliable crop recommendations,” Marlina noted.
The study’s findings underscore the critical role of climatic factors, particularly rainfall and humidity, in determining crop suitability. Macronutrients like potassium, phosphorus, and nitrogen also played significant roles, while temperature and soil pH had a relatively lower impact. This insight could reshape how farmers approach land management and crop cultivation strategies.
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. By leveraging advanced ensemble learning techniques, farmers can reduce the risks of crop failure and improve overall productivity. “This technology has the potential to transform the agriculture sector by providing data-driven insights that optimize resource use and enhance sustainability,” Marlina explained. The adoption of such systems could lead to more efficient use of fertilizers, water, and other resources, ultimately benefiting both farmers and the environment.
Looking ahead, the study’s findings could pave the way for further advancements in agricultural technology. As Marlina suggests, “Future research could explore the integration of real-time data and IoT devices to enhance the accuracy and applicability of crop recommendation systems.” This could lead to more dynamic and responsive systems that adapt to changing environmental conditions in real time.
In conclusion, the research highlights the potential of ensemble learning techniques to optimize crop recommendation systems, offering a promising avenue for enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability. As the agriculture sector continues to embrace data-driven approaches, the insights from this study could play a pivotal role in shaping the future of farming.