In the rapidly evolving world of agriculture, digital transformation is emerging as a powerful tool to enhance risk management in supply chains, ultimately boosting efficiency and resilience. A recent study published in *Agriculture & Food Security* delves into this very topic, offering insights that could reshape how the agriculture sector approaches risk management.
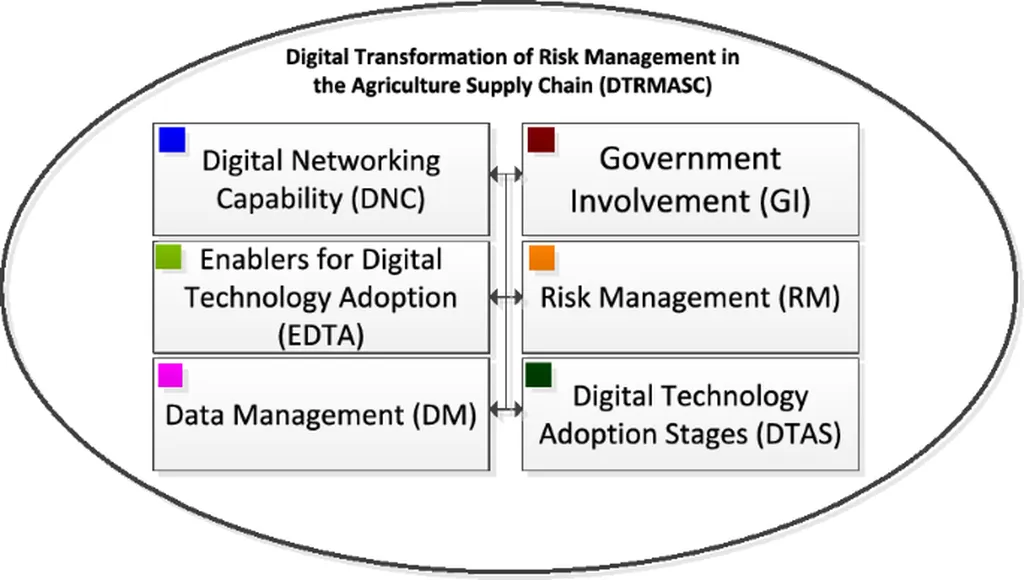
The research, led by R. D. H. Lumbantobing from the School of Business and Management at the Bandung Institute of Technology, employs a system dynamics approach to unravel the complexities of digital transformation in risk management for agriculture supply chains (RMASC). The study highlights the multifaceted nature of this transformation, which involves a web of interrelated components that dynamically influence each other.
“Digital transformation offers innovative opportunities for enhancing risk management in the agriculture supply chain,” Lumbantobing explains. “However, the process is challenging due to its complexity and the dynamic behavior of the system.”
The study identifies key components of the digital transformation of RMASC (DTRMASC) system, including government involvement, enablers for digital technology adoption, digital networking capability, data management, risk management, and digital advancement processes. By using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to assign variable weights, the researchers formulated relationships between these components.
One of the most compelling aspects of this research is its use of simulation to explore strategies for improving DTRMASC. The study presents three scenario categories: risk management without leveraging digital technology, the baseline of DTRMASC, and an improved DTRMASC. The findings reveal that accelerating the adoption of digital technology and increasing the enablers of the digital agriculture supply chain are primary triggers for improved digital transformation.
“Policy, ethical issues, and operational costs are the top three factors that influence digital technology preference,” Lumbantobing notes. This insight could be invaluable for policymakers and stakeholders looking to navigate the complexities of digital transformation in the agriculture sector.
The commercial implications of this research are significant. By enhancing risk management through digital transformation, agriculture supply chains can become more efficient and resilient, ultimately leading to improved profitability and sustainability. The study’s findings could guide stakeholders in evaluating and planning their digital transformation strategies, highlighting areas that require further improvement.
As the agriculture sector continues to evolve, the insights from this research could shape future developments in risk management and digital transformation. By understanding the dynamic nature of DTRMASC and its primary triggers, stakeholders can make informed decisions that drive progress and innovation in the field.