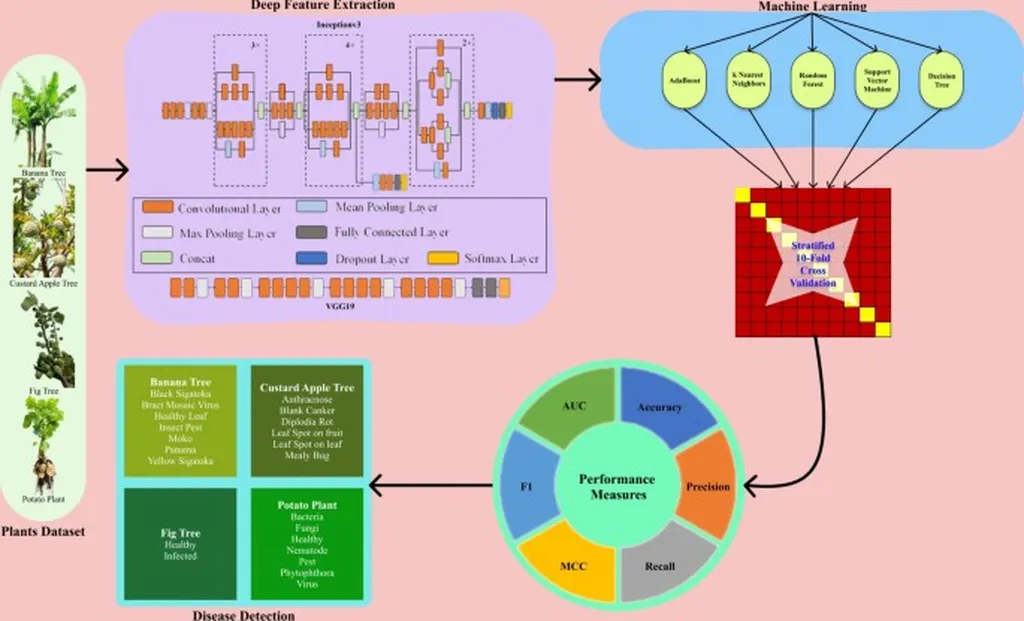
In a groundbreaking development for the agricultural sector, researchers have introduced a novel deep learning framework designed to significantly improve the detection of plant diseases. This pioneering study, led by a team of scientists including Rahaman, Paul, and Chowdhury, leverages the advanced MobileNetV3Large architecture, marking a substantial advancement in the application of machine learning to agricultural challenges.
The MobileNetV3Large architecture, known for its efficiency and versatility, is particularly suited for mobile and edge applications. Its ability to deliver high accuracy while maintaining a lightweight model is crucial for deployment in resource-constrained environments, a common scenario in agricultural settings. The researchers customized the MobileNetV3Large model to prioritize both precision and efficiency in identifying a wide range of plant diseases. This optimization is vital for timely interventions that can save crops and secure farmers’ livelihoods.
The importance of effective plant disease detection extends beyond individual farms, impacting food security, farmer income, and ecosystem health. Traditional methods of disease identification, which often rely on human expertise, can be time-consuming and prone to error. By integrating deep learning techniques, the research aims to automate and enhance the detection process, ensuring rapid and accurate identification of diseases. This enables prompt intervention measures that can significantly mitigate crop losses.
The researchers utilized a comprehensive dataset comprising images of various plants affected by multiple diseases. This diverse dataset was essential for training the deep learning model, ensuring it could generalize effectively across different species and disease types. The meticulous curation and labeling of the dataset underscore the importance of high-quality data in machine learning applications.
During the experimental phase, the researchers employed various optimization techniques, including hyperparameter tuning, data augmentation, and transfer learning. These strategies were crucial for improving the model’s accuracy and robustness, ensuring its effectiveness in real-world applications where data variability is common.
Addressing the challenges of deploying deep learning models in agricultural settings, the team considered technical limitations such as hardware compatibility, environmental factors, and the need for real-time processing. By ensuring the model’s functionality on mobile devices, they have made the technology accessible to farmers in the field, regardless of robust infrastructure. This accessibility is vital for improving the technology’s usability across different geographical regions, particularly in resource-limited areas.
A significant highlight of this research is its potential for early disease detection, which can transform crop health management and minimize losses. By enabling farmers to identify diseases at their nascent stages, the framework reduces reliance on chemical treatments, promoting sustainable agricultural practices. The benefits extend to supply chains and market stability, ensuring healthier crops reach consumers.
The findings of this research align with global discussions on food security and sustainability. As the world faces challenges from climate change and population growth, innovative solutions like this deep learning framework become increasingly relevant. The technology bridges traditional agricultural practices with modern advancements, fostering resilience in food systems worldwide.
The research team is exploring partnerships with stakeholders in the agricultural sector, including local governments, NGOs, and farming cooperatives. Collaboration is essential for effectively implementing the technology and ensuring it meets the needs of the farming community. By working directly with farmers, the team aims to refine the application, gathering feedback to inform future iterations and enhance its practical utility.
The advent of a MobileNetV3Large-based deep learning framework for detecting plant diseases represents a pivotal moment in agricultural technology. The work of Rahaman, Paul, and Chowdhury not only signifies a scientific achievement but also reflects a commitment to advancing sustainable agricultural practices. The potential impact on food security and crop health management is profound, and as this research progresses, it could set a new standard for innovations within the agricultural domain. The future looks promising for farmers and researchers embracing these technological advancements, paving the way for improved agricultural outcomes globally.
This study will be published in the upcoming issue of the journal “Discov Artif Intell” in 2026, amid growing interest in applying machine learning to practical challenges in various fields. With continuous advancements in technology, further developments in deep learning applications are anticipated, promising a future where agriculture and technology harmoniously coexist to address some of the most pressing challenges faced by the industry.