In the ever-evolving world of functional beverages, a recent study has shed light on a promising fusion of tradition and innovation: Curcuma xanthorrhiza kombucha. This research, published in *Advances in Food Science, Sustainable Agriculture, and Agroindustrial Engineering*, explores how the addition of Curcuma xanthorrhiza extract can enhance the functional properties of kombucha, a fermented tea known for its probiotic benefits.
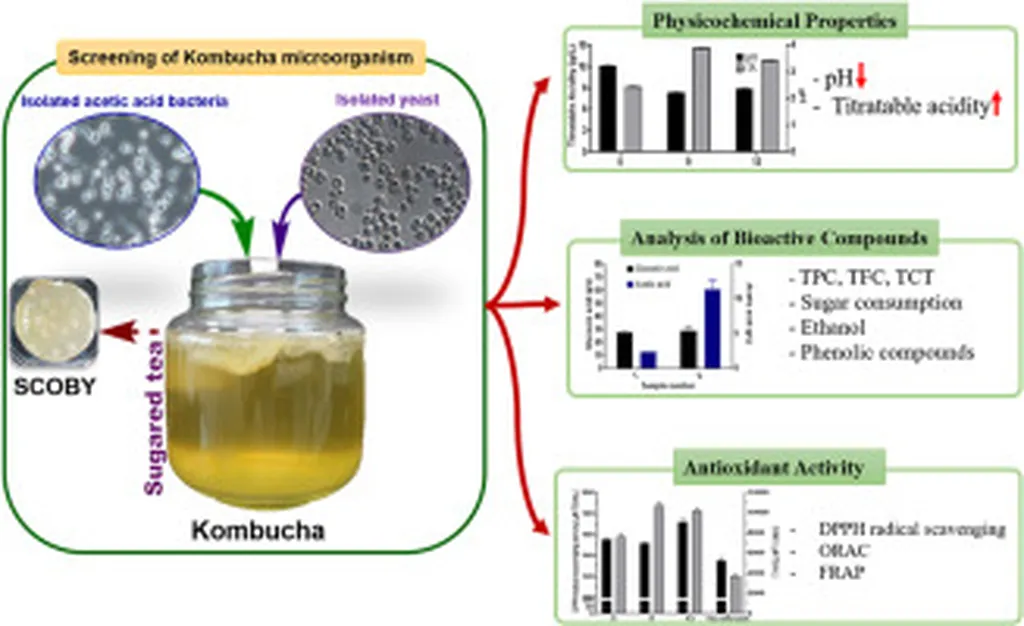
Kombucha, a beverage with ancient roots, is created through the symbiotic action of yeasts and bacteria. The study, led by Yunita Khilyatun Nisak from Universitas Nahdlatul Ulama Pasuruan, investigated the impact of Curcuma xanthorrhiza extract on the physicochemical characteristics, antioxidant activity, and metabolite profile of kombucha. The findings are intriguing and hold significant potential for the agriculture and food industries.
The research team prepared kombucha beverages with varying concentrations of Curcuma xanthorrhiza extract (0.4–2% w/v) and compared them to a control group made with black tea. The fermentation process lasted 12 days, during which the pH levels decreased significantly, indicating active microbial metabolism and the production of organic acids. “The decrease in pH and the increase in titratable acidity suggest that the microorganisms are thriving and producing beneficial compounds,” Nisak explained.
One of the most notable findings was the improvement in antioxidant activity. The IC₅₀ values, which measure the concentration of a substance required to inhibit a specific biological or biochemical function by 50%, dropped dramatically. In the control group, the IC₅₀ value decreased from 11.9 mg/mL at day 0 to 0.18 mg/mL after fermentation. For the Curcuma treatments, the values ranged from 4.54 mg/mL to 0.61–0.94 mg/mL post-fermentation. This enhancement in antioxidant activity suggests that Curcuma xanthorrhiza kombucha could be a powerful tool in promoting health and wellness.
Metabolite profiling using liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry (LC–HRMS) revealed a rich array of bioactive compounds. Over 40 compounds were identified, including gluconic acid, citric acid, ferulic acid, vanillic acid, flavonoids, and curcumin derivatives unique to the Curcuma treatments. These compounds contribute to the beverage’s functional properties and could attract health-conscious consumers.
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. As the demand for functional foods and beverages continues to grow, the integration of medicinal plants like Curcuma xanthorrhiza into traditional products like kombucha could open new avenues for farmers and food manufacturers. “This study highlights the potential for agricultural products to be transformed into high-value, health-promoting beverages,” Nisak noted. “It’s an exciting opportunity for the agriculture sector to diversify and tap into the growing market for functional foods.”
The findings also pave the way for further research into the synergistic effects of different plant extracts and fermentation processes. Understanding how these interactions can enhance the nutritional and functional properties of beverages could lead to the development of new products that cater to a wide range of health needs.
In conclusion, the study on Curcuma xanthorrhiza kombucha offers a glimpse into the future of functional beverages. By combining traditional fermentation techniques with modern scientific analysis, researchers have uncovered a wealth of potential benefits that could revolutionize the food and agriculture industries. As consumers increasingly seek out products that promote health and well-being, the integration of medicinal plants into everyday beverages could become a key trend in the years to come.