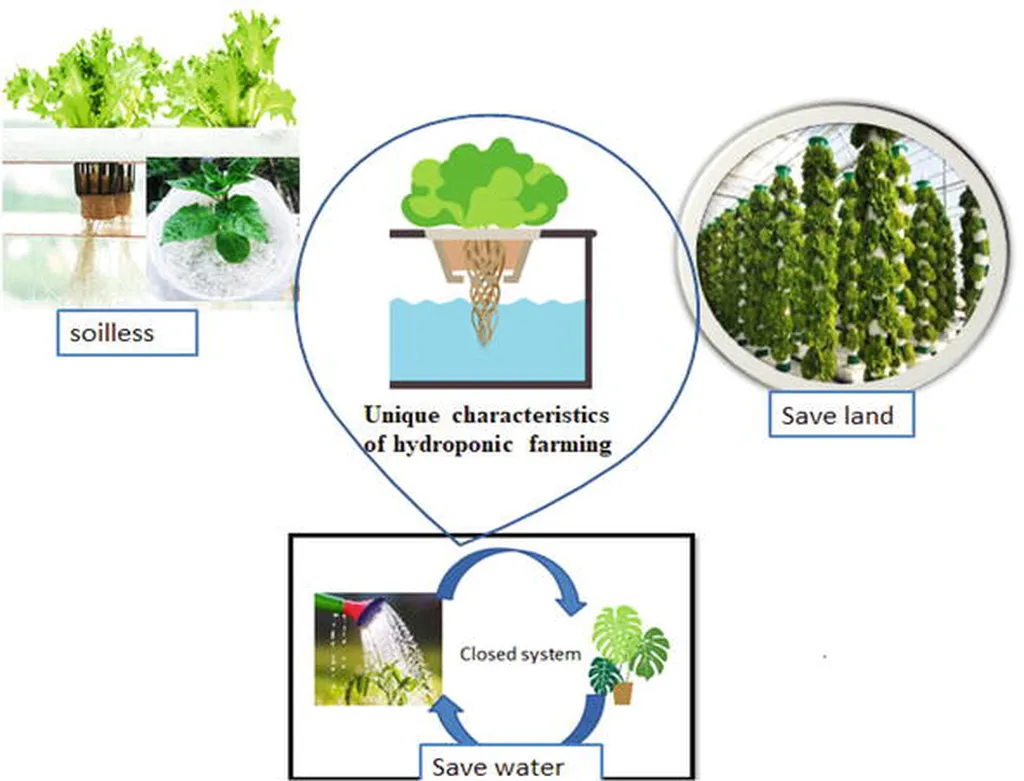
In the quest to merge productivity with sustainability, researchers have turned to hydroponics as a promising alternative to traditional agriculture. However, the challenge lies in finding biodegradable materials that offer the right balance of mechanical strength, stability, and compatibility with nutrient solutions. A recent study published in *Materials Research* tackles this issue head-on, proposing innovative composites that could revolutionize hydroponic systems.
The research, led by Renato de Sousa Nascimento Júnior, focuses on developing composites based on poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), a biodegradable polymer. The team functionalized PBAT with activated carbon (AC) and the cationic surfactant CTAB, aiming to enhance its properties for hydroponic applications. The formulations—PBAT, PBAT/5AC, PBAT/5AC/1CTAB, and PBAT/5AC/2CTAB—were processed through extrusion and injection, then characterized using mechanical testing, thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, and contact angle measurements.
The results are promising. CTAB acted as a functionalizing agent, improving the dispersion of activated carbon and reducing agglomerates. This led to a 15.53% increase in the modulus of elasticity and a 4.05% boost in tensile strength. Moreover, the composites exhibited greater surface hydrophilicity, which is crucial for adhesion to aqueous solutions. “The addition of CTAB not only enhanced the mechanical properties but also improved the surface characteristics, making the composites more suitable for hydroponic systems,” Nascimento Júnior explained.
While the thermal stability of the composites was slightly lower, the overall properties make them a strong candidate for sustainable substrates and components in hydroponic cultivation. This research could pave the way for more eco-friendly and efficient agricultural practices, addressing the growing demand for sustainable food production.
The implications for the agriculture sector are significant. As hydroponic systems gain traction, the need for biodegradable and high-performance materials becomes increasingly important. These composites could offer a viable solution, reducing the environmental impact of agriculture while maintaining productivity. “This study opens up new possibilities for the development of sustainable materials that can support the growth of hydroponic systems,” Nascimento Júnior added.
The research, published in *Materials Research* and led by Nascimento Júnior, represents a step forward in the quest for sustainable agriculture. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and resource depletion, innovations like these are crucial. They not only advance the field of agritech but also contribute to a more sustainable future for all.