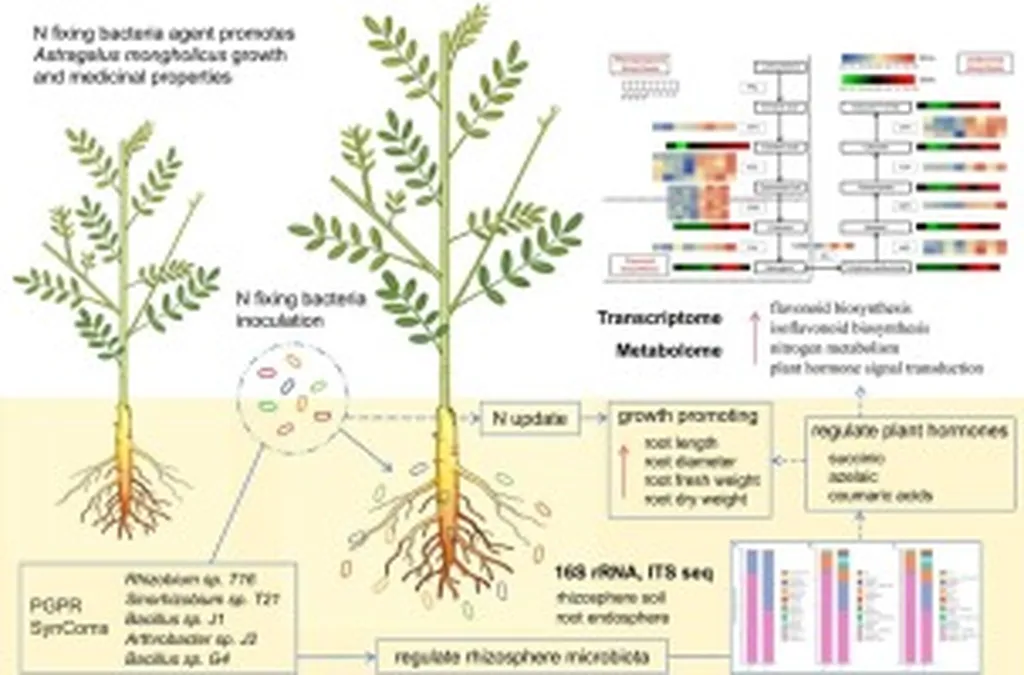
In the quest for sustainable agriculture, scientists are increasingly turning to the microscopic world for solutions. A recent study published in *Industrial Crops and Products* has uncovered how a nitrogen-fixing bacterial agent can significantly enhance the growth and medicinal properties of Astragalus mongholicus, a valuable medicinal plant. The research, led by Shi Zhiyong from the College of Life Sciences at Shanxi Agricultural University, offers promising insights into the future of precision agriculture and sustainable crop cultivation.
Astragalus mongholicus, known for its medicinal properties, faces challenges in cultivation due to soil fertility and microbial interactions. The study investigated the impact of a mixed nitrogen-fixing bacterial agent on the plant’s root physiology, metabolite profiles, gene regulation, and microbial communities. The findings reveal a complex interplay between the bacterial agent and the plant, highlighting the potential for microbial interventions to revolutionize agricultural practices.
“Our integrative multi-omics analyses showed that the inoculation of the nitrogen-fixing bacterial agent shifts the microbial community in the rhizosphere,” explained Shi Zhiyong. “This shift produces plant hormones that promote growth, regulate secondary metabolism, and enhance stress resistance, suggesting synergistic microbial-plant interactions.”
The study found that genes linked to secondary metabolism, stress tolerance, plant hormone signal transduction, and nitrogen metabolism were up-regulated in A. mongholicus. Key metabolites, including succinic acid and flavonoids, showed significant increases, correlating with enhanced medicinal compound accumulation. These findings suggest that microbial interventions can modulate root metabolism and microbiome composition, offering a sustainable strategy for improving crop yield and quality.
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. As the demand for medicinal plants continues to grow, farmers and agricultural companies are seeking sustainable and efficient ways to enhance crop production. The use of nitrogen-fixing bacterial agents could reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, lower production costs, and improve the quality of medicinal crops. This approach aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable and precision agriculture, where targeted interventions can maximize yield and quality while minimizing environmental impact.
“This work demonstrates that microbial interventions can modulate root metabolism and microbiome composition, offering a sustainable strategy for improving A. mongholicus yield and quality,” Shi Zhiyong noted. “The findings highlight the potential of bioactive microbial agents in precision agriculture.”
The research published in *Industrial Crops and Products* not only sheds light on the intricate relationships between microbes and plants but also paves the way for future developments in the field. As scientists continue to explore the microbial world, the potential for innovative agricultural solutions grows. The study led by Shi Zhiyong from the College of Life Sciences at Shanxi Agricultural University and Shanxi Key Laboratory of Chinese Veterinary Medicine Modernization offers a glimpse into a future where microbial interventions play a crucial role in sustainable agriculture.