In the ever-evolving landscape of modern agriculture, the quest for efficient pest management and food safety has led to groundbreaking advancements in pesticide formulations and residue analysis. A recent review published in *Review of Materials Research* sheds light on the transformative potential of nanocomposites in revolutionizing pesticide delivery systems and analytical techniques. Led by Dasari Ayodhya of the Chemical Group at the Intellectual Property India Patent Office in Chennai, this research offers a comprehensive look at how nanotechnology is reshaping the agricultural sector.
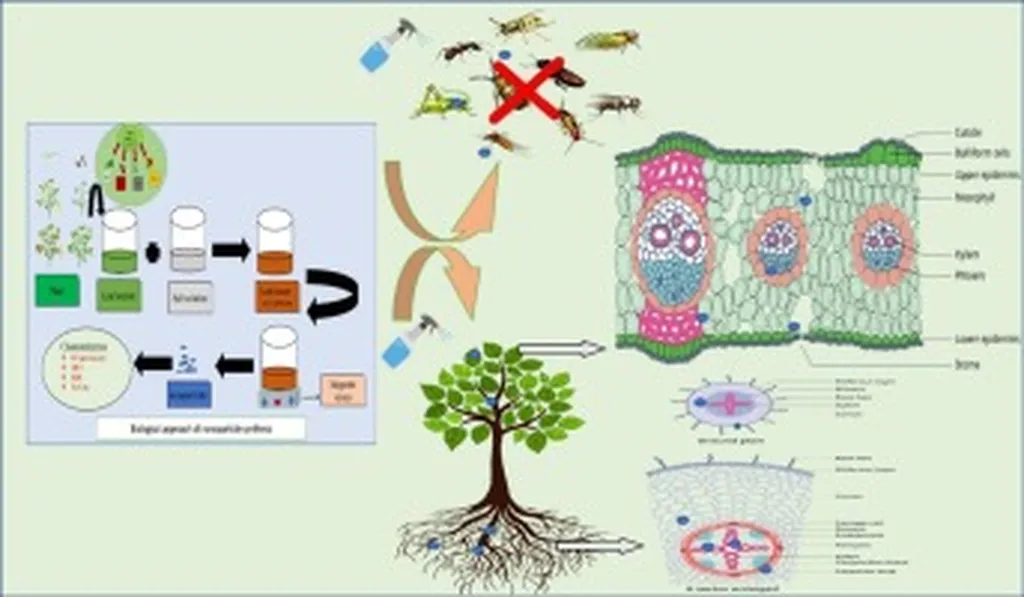
The study highlights the rapid growth of pesticide usage in modern agriculture, which has necessitated innovative strategies to enhance pest management efficiency while ensuring food safety and environmental protection. Nanocomposites, with their unique properties, have emerged as a game-changer in this arena. These advanced materials improve the stability, targeted delivery, controlled release, and bioavailability of active ingredients in pesticides. “The integration of nanocomposites into pesticide formulations represents a significant leap forward in agricultural technology,” says Ayodhya. “These nanoformulations not only enhance the effectiveness of pest control but also minimize environmental impact.”
The review delves into a variety of nanocomposite-based pesticide formulations, including chitosan, clay, silicon, polymer, carbon dot, metal, metal oxide, and graphene-based systems. Additionally, it explores advanced water-dispersible systems such as nanocapsules, nanoemulsions, nanospheres, nanomicelles, and nanosuspensions. These innovations are poised to revolutionize pest management by providing more precise and sustainable solutions.
One of the critical aspects addressed in the review is the importance of pesticide residue analysis. Ensuring food safety, regulatory compliance, and environmental monitoring are paramount in the agricultural sector. The study critically examines various analytical approaches for residue detection, including chromatographic methods like HPLC, LC–MS, GC–MS, MS/MS, and HRMS, as well as spectroscopic techniques such as UV–Vis, FTIR, Raman, NMR, fluorescence, NIR, and ICP. Immunoassay-based tools like ELISA and ICA are also discussed, highlighting their roles in efficient sample preparation across diverse food matrices.
The review further discusses contemporary extraction and cleanup technologies such as SPE, SPME, SBSE, QuEChERS, DLLME, MAE, PLE, and supercritical fluid extraction. These methods play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability of analytical outcomes, addressing parameters like selectivity, linearity, sensitivity, accuracy, precision, robustness, and stability.
The implications of this research extend beyond immediate applications. The study also explores emerging knowledge on pesticide degradation pathways and nanomaterial-assisted monitoring strategies. “Understanding these pathways is essential for developing more effective and environmentally friendly pest management solutions,” notes Ayodhya. The biosafety implications of nanoformulations and their influence on degradation kinetics are also critically evaluated, providing a holistic understanding of the field.
As the agricultural sector continues to evolve, the integration of material science, analytical chemistry, and agricultural practices offers a promising path forward. This research not only highlights the current advancements but also sets the stage for future developments in sustainable and safe agricultural production. With the insights provided by Dasari Ayodhya and his team, the agricultural industry is better equipped to meet the challenges of pest management and food safety in the years to come.