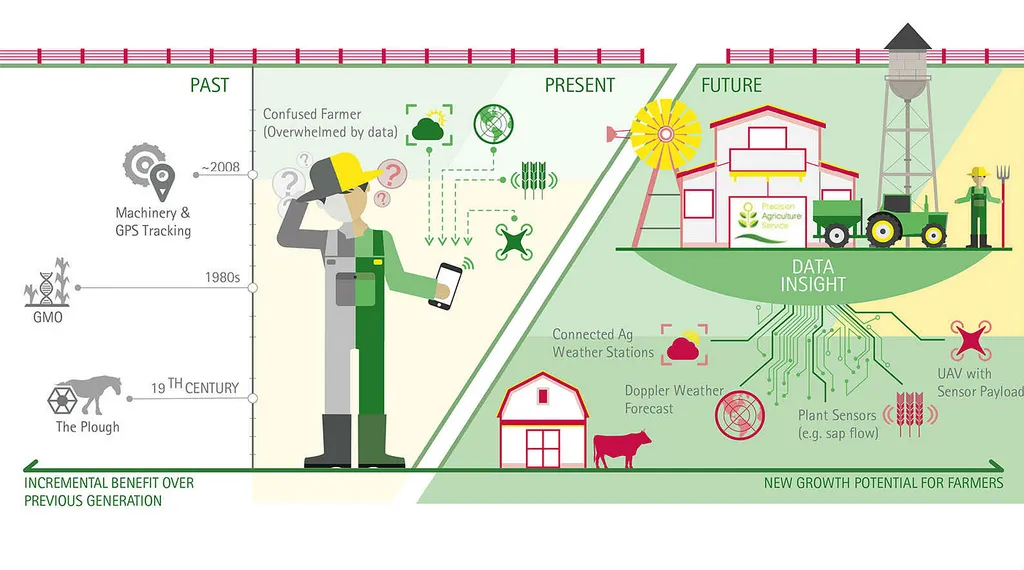
In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, technology adoption is a critical factor in addressing global food security, climate resilience, and rural livelihoods. A recent study published in *Advancements in Agricultural Development* offers a fresh perspective on this challenge by combining classic theory with cutting-edge machine learning techniques. Led by Jaehyun Ahn of the University of Florida, the research systematically reviews agricultural technology adoption from 2021 to 2025, integrating Everett Rogers’ diffusion of innovation theory with a Random Forest (RF) analysis to identify key adoption drivers.
The study analyzed 571 cases from 531 publications, employing a rigorous methodology that included bibliometric searches, textual coding, and numerical conversion. The RF model, known for its predictive power, revealed that extension access, climate risk awareness, and perceived relative advantage—alongside perceived simplicity and training participation—are the most influential factors in adoption decisions. “Extension messages and programs should emphasize clear, observable benefits, manageable complexity, and climate-related risk information that directly addresses farmers’ needs and concerns,” Ahn explains.
While education and innovation literacy emerged as essential in specific contexts, their influence varied across cases. Peer networks, too, played a moderate but context-dependent role. These findings suggest that tailored extension strategies could significantly enhance technology adoption rates, ultimately boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. For agribusinesses and policymakers, understanding these adoption drivers can inform more effective marketing, training, and policy strategies. By focusing on the factors that matter most—such as ease of use, clear benefits, and climate relevance—companies can design technologies that resonate with farmers and accelerate their uptake. “This integrated methodological approach provides robust and nuanced insights, offering practical guidance for agricultural development policy, extension strategies, and future research,” Ahn notes.
As the agriculture sector continues to grapple with climate change, food security, and economic challenges, this research offers a roadmap for fostering innovation. By leveraging data-driven insights, stakeholders can create more impactful technologies and strategies, ensuring that agricultural advancements reach those who need them most. The study not only advances our understanding of technology adoption but also paves the way for more effective, farmer-centered solutions in the years to come.