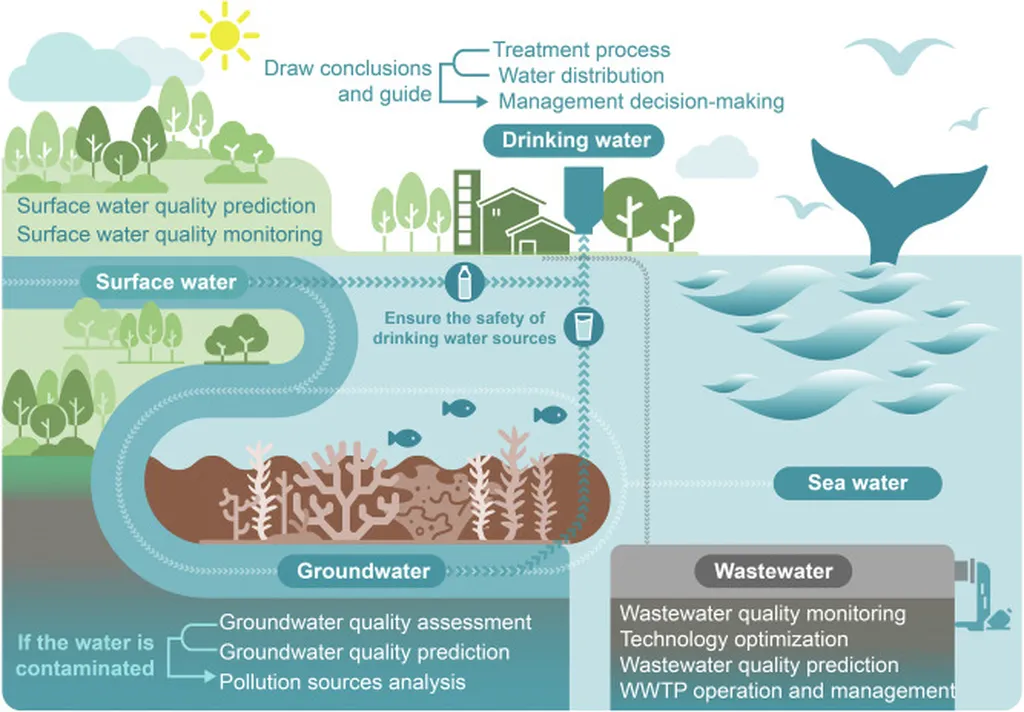
In the face of escalating environmental challenges and the pressing need for sustainable water management, a recent study published in ‘Вісник Харківського національного університету імені В.Н. Каразіна: Серія Екологія’ sheds light on modern trends in water quality forecasting, offering valuable insights for the agriculture sector and beyond. Led by V. V. Terzeman from I.I. Mechnikov Odesa National University, the research provides a comprehensive analysis of contemporary forecasting methods, their advantages, and their potential applications in Ukraine’s current context.
The study, which employed a systematic review approach according to the PRISMA methodology, reveals that artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) methods have emerged as the most common and promising techniques for water quality forecasting. “The use of AI and ML in water quality forecasting is not just a trend; it’s a significant leap forward in our ability to predict and manage water resources effectively,” Terzeman asserts.
For the agriculture sector, which is heavily reliant on water resources, these advancements could not come at a better time. Accurate water quality forecasting can help farmers optimize irrigation, reduce water waste, and minimize the use of fertilizers and pesticides, leading to improved crop yields and reduced environmental impact. Moreover, in the context of Ukraine’s full-scale war, where physical access to water bodies is often limited or impossible, remote sensing combined with machine learning offers a viable solution for monitoring and predicting water quality.
The research also highlights the potential of Explainable AI (XAI) methods to overcome the “black box” problem in water quality forecasting. Although XAI is primarily used in the agricultural sector in Ukraine, its application in water quality forecasting could enhance transparency and trust in AI-driven predictions. “The integration of XAI in water quality forecasting could revolutionize the way we understand and interpret complex environmental data,” Terzeman suggests.
As the world grapples with climate change and water scarcity, the insights from this study could shape future developments in water management and agriculture. By embracing AI and ML technologies, stakeholders can make data-driven decisions that promote sustainable water use and enhance agricultural productivity. The research underscores the importance of investing in advanced technologies to tackle pressing environmental challenges and secure a sustainable future for all.
In the words of Terzeman, “The future of water quality forecasting lies in the effective application of AI and ML methods, tailored to the unique needs and challenges of each region.” As the agriculture sector continues to evolve, the integration of these advanced technologies could pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient future.