In the ever-evolving landscape of agricultural technology, a groundbreaking review published in *NG Agricultural Sciences* is poised to reshape our understanding of plant nanotechnology and its synergy with artificial intelligence (AI). Led by A. El-Shabasy from the Department of Biology at Jazan University in Saudi Arabia, the research delves into 13 key thematic areas, offering a comprehensive overview of how AI can revolutionize plant nanotechnology for sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship.
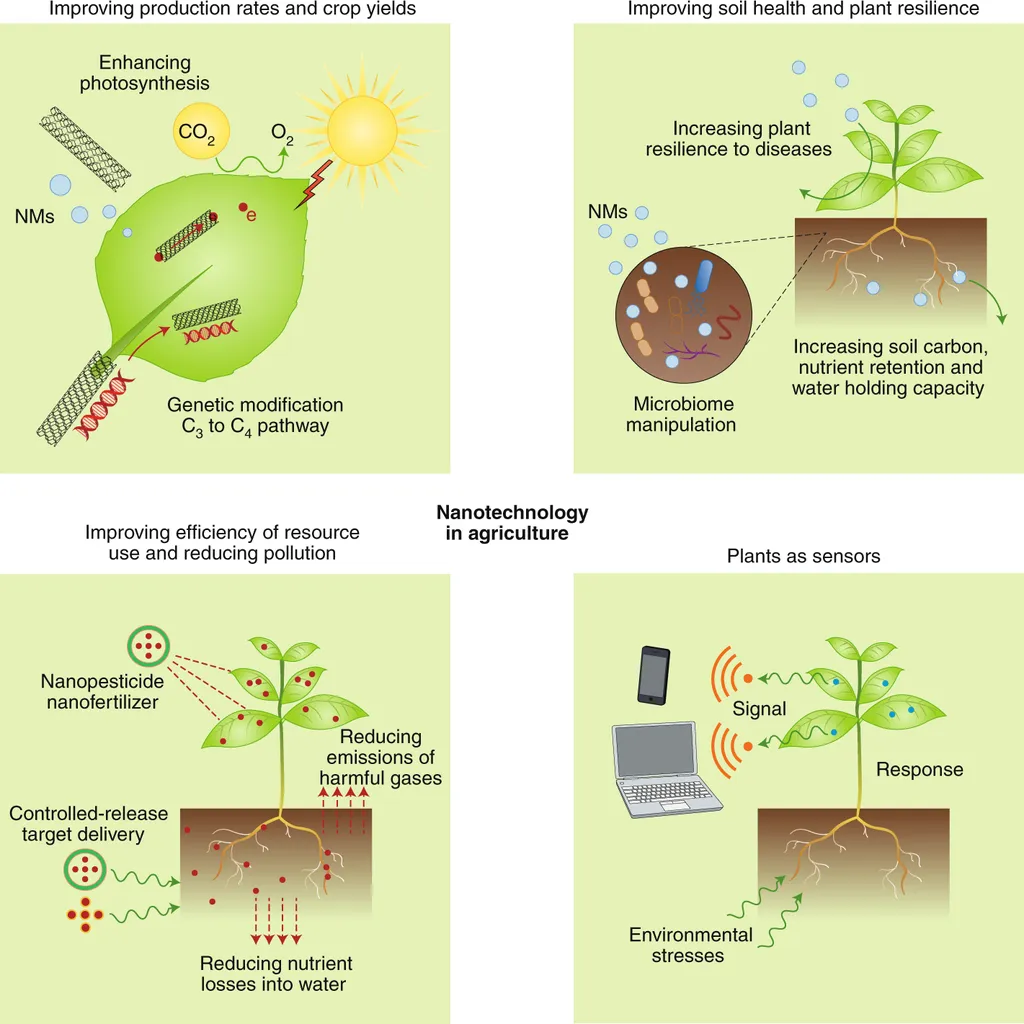
The study highlights the potential of nanotechnology in plants to optimize monitoring of both abiotic and biotic parameters, thereby enhancing resource efficiency and reducing environmental contamination. “Nanotechnology-enabled breeding technologies and the prospect of proteomics hold immense promise in boosting plant resilience and yields,” El-Shabasy noted, underscoring the transformative potential of these advancements.
One of the most compelling aspects of the review is its comparison of Non-Artificial Intelligent Digital Nano-manufacturing (NAIDNM) with Artificial Intelligent Digital Nano-manufacturing (AIDNM). This comparison not only presents the challenges inherent in both approaches but also offers potential solutions and future directions. The findings emphasize the significant contribution of AI-aided plant nanotechnology in improving productivity, resilience, and sustainability, addressing universal food security and ecological balance.
The commercial implications for the agriculture sector are profound. By integrating AI with nanotechnology, farmers can expect enhanced precision in irrigation, disease control, and soil health management. This integration can lead to more efficient use of resources, reduced environmental impact, and ultimately, higher crop yields. The review also touches on the broader environmental benefits, including the assessment of environmental risks, climate change forecasting, nutrient flow, and food web dynamics.
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and food security, the insights provided by El-Shabasy’s research offer a beacon of hope. The study not only highlights the current advancements but also paves the way for future developments in the field. By embracing AI and nanotechnology, the agriculture sector can look forward to a more sustainable and resilient future, ensuring food security for generations to come.
In the words of El-Shabasy, “The integration of AI and nanotechnology in agriculture is not just a technological leap; it’s a paradigm shift that can redefine our approach to sustainable farming and environmental conservation.” This review, published in *NG Agricultural Sciences*, serves as a testament to the transformative power of these technologies, offering a roadmap for the future of agriculture.