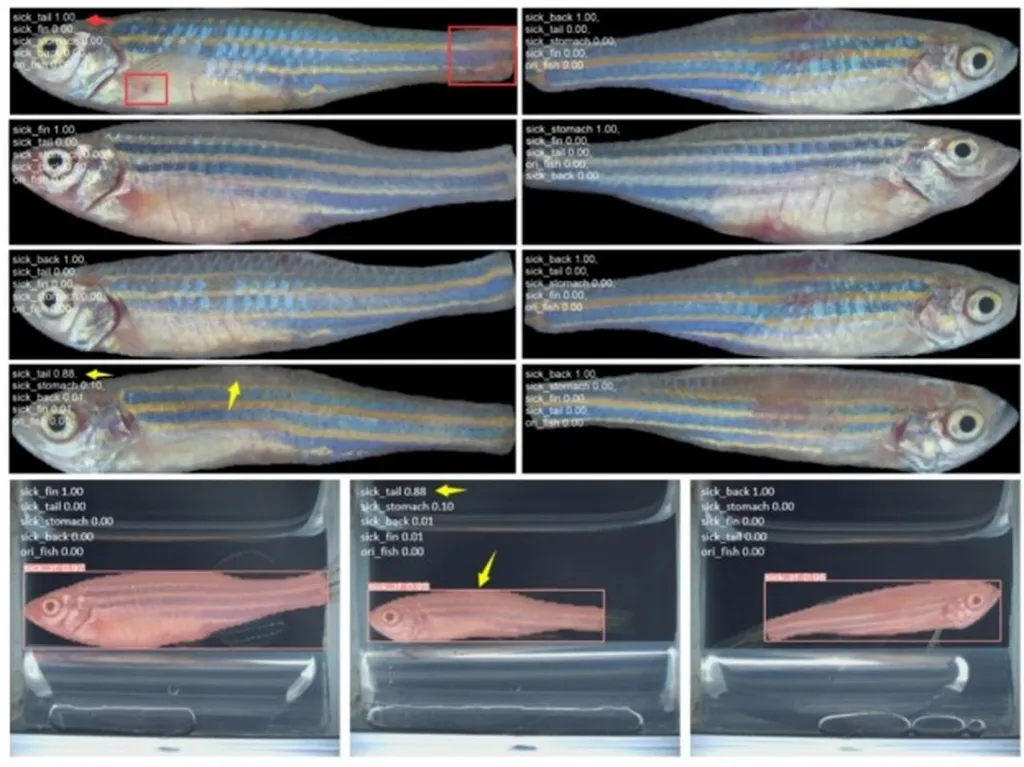
In the realm of aquaculture and fish health monitoring, a groundbreaking advancement has emerged that promises to revolutionize the way we detect and manage surface anomalies in fish. Researchers, led by Danying Cao from the Key Laboratory of Breeding Biotechnology and Sustainable Aquaculture at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a novel framework called ESC-YOLOv8-seg. This innovative method is set to enhance the precision and speed of detecting surface abnormalities in small fish, particularly zebrafish, which are widely used in medical, genetic, and environmental toxicology research.
The ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework is built upon the YOLOv8 architecture, a state-of-the-art object detection system known for its efficiency and accuracy. By integrating several advanced modules—EMA, SPPELAN, and C2f-Faster—the researchers have significantly improved the detection capabilities of the system. Additionally, they introduced an extra detection head (P2) specifically optimized for the extreme small target size of zebrafish, ensuring that even the most subtle anomalies are not overlooked.
One of the most compelling aspects of this research is its non-destructive nature. Traditional methods of fish disease detection often involve invasive procedures that can have irreversible effects on the fish, especially small species like zebrafish. The ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework, however, provides a real-time, non-destructive early warning system that can monitor fish health without causing any harm. This is a game-changer for the aquaculture industry, where the welfare of fish is paramount.
“The integration of positional information and surface features enables our method to achieve real-time monitoring and non-destructive early warning of fish surface abnormalities,” said Danying Cao. “This not only enhances the precision in small target detection but also achieves high accuracy in discerning subtle differences among detection targets.”
In real aquaculture settings, the ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework has demonstrated an impressive average speed of 106 frames per second (FPS) with a detection accuracy of 98%. These figures highlight the system’s potential for widespread adoption in the aquaculture industry, where real-time monitoring and early detection of fish health issues are crucial for preventing disease outbreaks and ensuring the overall welfare of the fish.
The implications of this research extend beyond zebrafish and aquaculture. The ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework is highly generalizable and can be applied to the real-time detection of underwater surface abnormalities in a range of fish species. This versatility makes it a valuable tool for various applications in the energy sector, particularly in monitoring the environmental impact of aquatic ecosystems.
Published in the journal ‘Ecological Informatics’ (生态信息学), this research represents a significant step forward in the field of computer vision and small target detection. As the demand for intelligent management and detection systems continues to grow, the ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of aquaculture and environmental monitoring.
The commercial impacts of this research are substantial. By providing a non-destructive, real-time monitoring system, the ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework can help aquaculture facilities reduce losses due to disease outbreaks and improve the overall health and welfare of their fish. This, in turn, can lead to increased productivity and profitability for the industry.
Moreover, the framework’s ability to detect subtle differences among detection targets can be invaluable in environmental toxicology research, where understanding the impact of various pollutants on aquatic life is crucial. By providing accurate and timely data, the ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework can help researchers and policymakers make informed decisions about environmental protection and conservation efforts.
In conclusion, the ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework developed by Danying Cao and her team represents a significant advancement in the field of fish health monitoring. Its non-destructive, real-time capabilities, and high accuracy make it a valuable tool for the aquaculture industry and environmental research. As the demand for intelligent management systems continues to grow, the ESC-YOLOv8-seg framework is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of these fields.