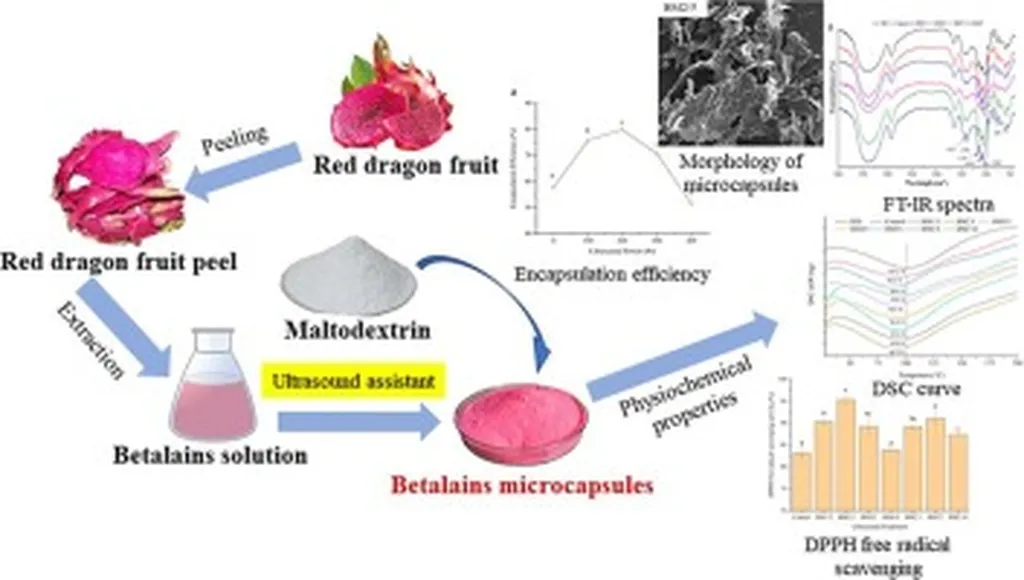
In a groundbreaking study published in the Jurnal Pangan dan Agroindustri, researchers from Universitas Brawijaya have unlocked new potential for the agricultural sector by enhancing the stability and commercial viability of betacyanin, a natural pigment found in red dragon fruit peels. Led by Sudarminto Setyo Yuwono, the research delves into the world of microencapsulation, a technology that could revolutionize how we utilize natural food colorants.
Betacyanin, known for its vibrant red hue, is highly sensitive to environmental factors like temperature and light, which limits its use in the food industry. To overcome this challenge, the team employed a microwave-assisted foam-mat drying method to create microcapsules that protect the betacyanin extract. “Microencapsulation is like giving betacyanin a protective shield,” explained Yuwono. “It allows us to preserve its color and stability, making it more suitable for commercial applications.”
The study explored the interaction between the ratio and concentration of two coating materials, maltodextrin and gum arabic, to determine the optimal conditions for microencapsulation. The researchers found that a coating ratio of 3:1 and a concentration of 15% w/v yielded the best results. These microcapsules exhibited superior solubility, yield, moisture content, and light stability compared to uncoated samples.
The implications for the agriculture sector are significant. Red dragon fruit peels, often discarded as waste, are now a valuable resource for natural food colorants. “This research not only reduces waste but also adds value to the agricultural supply chain,” noted Yuwono. By stabilizing betacyanin, the study opens doors to new markets and applications in the food and beverage industry, potentially boosting the economic returns for farmers and processors.
The findings could also inspire further innovation in the field of natural food colorants. As consumer demand for clean-label and natural ingredients grows, the need for stable and effective natural colorants becomes increasingly important. This research provides a blueprint for future developments, encouraging other scientists to explore similar techniques for other natural pigments.
In summary, the study by Yuwono and his team represents a significant step forward in the utilization of natural food colorants. By enhancing the stability of betacyanin through microencapsulation, they have unlocked new opportunities for the agriculture sector and paved the way for future innovations in the food industry. As the world continues to seek sustainable and natural solutions, this research offers a promising path forward.