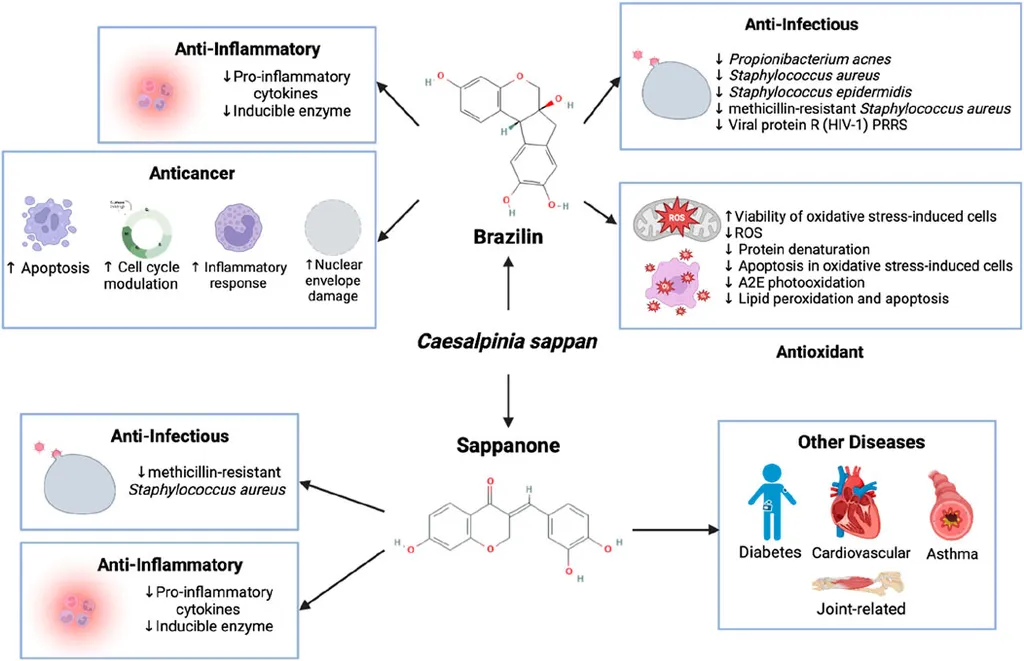
In the quest to combat postmenopausal obesity, a team of researchers led by Kanit Vichitphan from the Department of Biotechnology at Khon Kaen University in Thailand has uncovered promising potential in an unlikely source: sappan cider. Their study, recently published in *Cogent Food & Agriculture*, explores how fermenting the extract of Biancaea sappan L. Tod, a plant known for its antioxidant properties, could offer a novel approach to managing obesity in postmenopausal women.
Postmenopausal obesity is a significant health concern, characterized by increased visceral fat accumulation due to estrogen deficiency. Traditional treatments often come with side effects, prompting researchers to seek alternative solutions. Vichitphan and his team hypothesized that fermenting Biancaea sappan extract into sappan cider using a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) could enhance its biological activity.
The study involved 48 ovariectomized (OVX) female rats, divided into eight groups to test various treatments, including tamoxifen, Biancaea sappan extract, standard kombucha, and different doses of sappan cider. After 28 days of oral treatment, the results were striking. The highest dose of sappan cider (CID III) significantly reduced body weight gain, visceral fat mass, and adipocyte diameter compared to the OVX control group. Additionally, it enhanced superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) levels, indicating improved redox balance and reduced inflammation.
“Our findings suggest that SCOBY-fermented Biancaea sappan cider could be a potential nutraceutical for managing postmenopausal obesity,” Vichitphan explained. “The fermentation process not only converts brazilin to brazilein but also increases the total phenolic content, which may contribute to its enhanced biological activity.”
The implications for the agriculture sector are substantial. Biancaea sappan, commonly known as sappanwood, is a plant with a long history of medicinal use. Its potential as a nutraceutical could open new markets for farmers and agribusinesses, particularly in regions where the plant is cultivated. The study highlights the value of traditional plants in modern health solutions, encouraging further research into their potential applications.
Moreover, the use of SCOBY fermentation, a process already popular in the production of kombucha, could drive innovation in the food and beverage industry. As consumers increasingly seek out functional foods and beverages that offer health benefits, sappan cider could emerge as a novel product with significant commercial potential.
This research not only sheds light on a promising alternative for managing postmenopausal obesity but also underscores the importance of integrating traditional knowledge with modern science. As Vichitphan and his team continue to explore the potential of Biancaea sappan, the agricultural and health sectors alike may find new opportunities to grow and innovate.