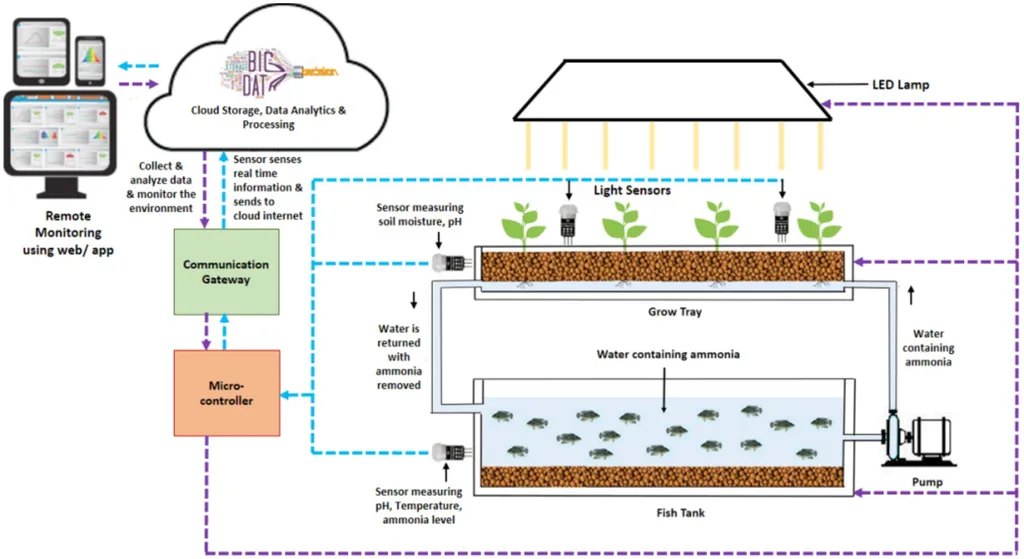
In the rapidly evolving world of agriculture, vertical farming has emerged as a promising frontier, offering the potential to revolutionize food production. A recent study published in *Scientific Reports* delves into the complexities of this innovative farming technique, providing a robust decision framework that could significantly impact the agriculture sector.
Vertical farming, which involves cultivating plants without soil, has gained traction due to its ability to produce high-quality yields with minimal resources. The study, led by Navaneethakrishnan Suganthi Keerthana from the Department of Mathematics at Bharathiar University, explores various vertical farming methods, including hydroponics, aquaponics, aeroponics, and fogponics. The research employs a novel hybrid approach, combining the q-rung picture fuzzy set with a Logarithmic percentage change-driven objective weighting and Multi-attributive border approximation area comparison framework. This method aims to quantify uncertainty and ambiguity, providing an objective analysis based on distance measures.
The study’s findings highlight the crucial role of production yield in selecting the optimal vertical farming technology. “Our research concludes that aquaponics is the most effective vertical farming method, followed by aeroponics, fogponics, and hydroponics,” Keerthana explained. This ranking is based on a comprehensive analysis that considers various factors, including resource efficiency and yield quality.
The implications of this research for the agriculture sector are substantial. Vertical farming, with its ability to produce high-quality yields in controlled environments, can address the growing demand for food while minimizing resource use. The study’s decision framework offers a valuable tool for farmers and investors, helping them make informed decisions about which vertical farming technology to adopt.
Moreover, the study’s methodology, which includes a comparison analysis and sensitivity analysis, ensures the reliability and accuracy of the results. “We conducted Spearman’s rank correlation to better understand the results of the comparison analysis,” Keerthana noted. This rigorous approach underscores the study’s potential to shape future developments in the field.
As the agriculture sector continues to evolve, research like this is crucial. It provides a roadmap for adopting innovative technologies that can enhance productivity and sustainability. The study’s findings could pave the way for a new era of vertical farming, one that is more efficient, profitable, and environmentally friendly.