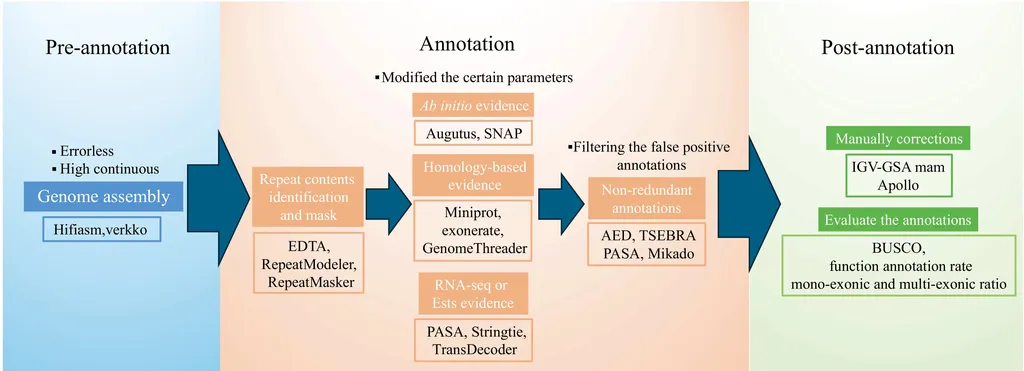
In the rapidly evolving world of agricultural biotechnology, the ability to accurately annotate genomes is becoming increasingly crucial. As sequencing technologies advance and genome assembly algorithms improve, researchers are now faced with the challenge of ensuring the accuracy of genome annotations, which serve as the foundation for downstream analyses. A recent study published in *Genomics Communications* offers practical tips to enhance the quality of genome annotation, potentially revolutionizing the way we approach agricultural genomics.
The study, led by Lan Lan from the State Agricultural Biotechnology Centre (SABC) at Murdoch University in Australia, highlights the importance of meticulous attention to detail during the genome annotation process. “Accurate genome annotation is the cornerstone for downstream analysis,” Lan emphasizes. “It’s not just about obtaining high-quality genome assembly results; the real challenge lies in ensuring the annotation is precise.”
The research outlines six key tips to reduce annotation errors, focusing on the nuances of widely used annotation tools and pipelines such as MAKER and EvidenceModeler. These tips include optimizing parameters, validating evidence, and ensuring consistency across different tools. By addressing these details, researchers can significantly improve the accuracy of their annotations, leading to more reliable downstream analyses.
The commercial impacts of this research for the agriculture sector are substantial. Accurate genome annotation is essential for identifying genes associated with desirable traits, such as disease resistance, drought tolerance, and yield improvement. This information is invaluable for plant breeders and genetic engineers, who rely on precise genetic data to develop better crop varieties. “Improving annotation quality can accelerate the breeding process and lead to more efficient and sustainable agricultural practices,” Lan notes.
The study also sheds light on the importance of choosing the right tools and pipelines for specific applications. Different tools may have unique strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these nuances can help researchers make informed decisions. For instance, MAKER is known for its comprehensive approach, integrating various types of evidence to improve annotation accuracy. On the other hand, EvidenceModeler excels in its ability to handle large-scale data sets efficiently.
As the field of agricultural genomics continues to evolve, the insights from this research could shape future developments. By improving the accuracy of genome annotations, researchers can unlock new possibilities for crop improvement, pest management, and environmental sustainability. The study serves as a reminder that attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the tools at hand are crucial for advancing the field.
In the words of Lan Lan, “The devil is in the details. By paying close attention to the annotation process, we can ensure that our genetic data is as accurate and reliable as possible, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries in agriculture.” With the publication of this study in *Genomics Communications*, the agricultural biotechnology community has a valuable resource to guide their efforts in improving genome annotation quality.