In the quest for sustainable agriculture, researchers are increasingly turning to biostimulants to enhance crop productivity and quality. A recent study published in *Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca* sheds light on the combined effects of biostimulants and phosphorus on muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) crops, offering promising insights for farmers and agronomists alike.
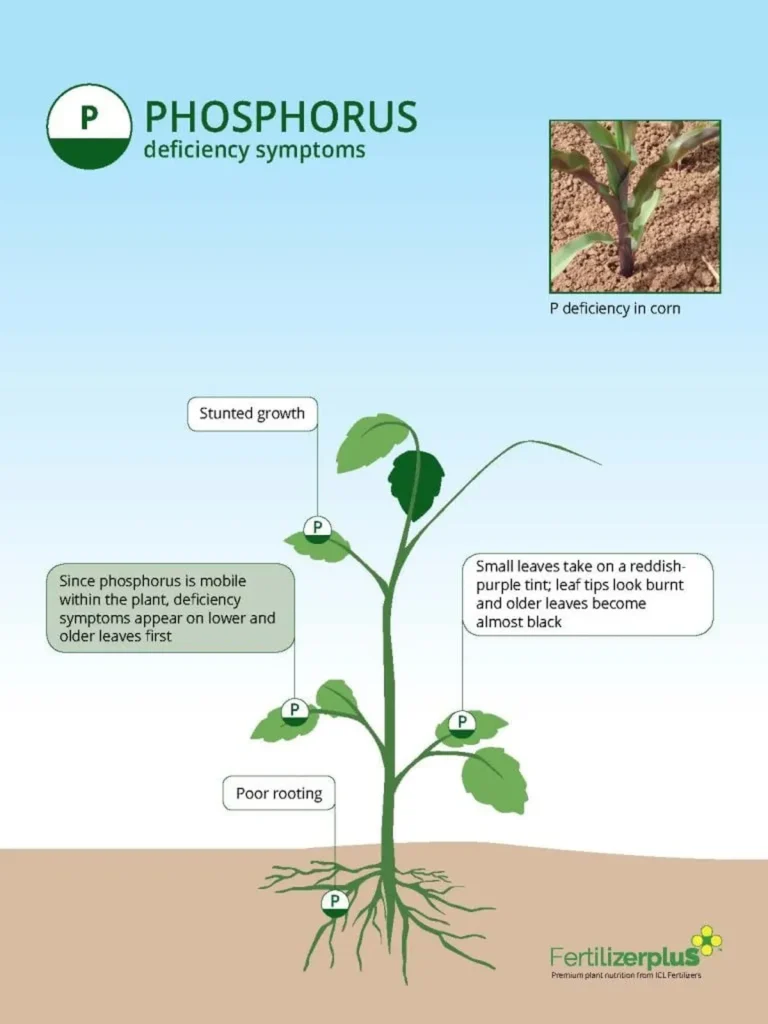
Muskmelon, a hydrating fruit packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, is a staple in tropical and subtropical regions. However, these regions often grapple with phosphorus (P) deficiency, which can significantly impact the fruit’s sugar and acid contents due to phosphorus’s role in sugar acid phosphatase enzymes. To address this challenge, researchers led by Gayathri Balusamy from the Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Department of Crop Physiology, Coimbatore, explored the potential of biostimulants, particularly phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria, to improve phosphorus use efficiency and enhance muskmelon yield and quality.
The study investigated the effects of three phosphorus levels (100%, 50%, and 0% P₂O₅) and biostimulants (control, GEA 1499—a formulation containing a plant-based biostimulant and the microbial species Bacillus pumilus and Bacillus megaterium at 2.5 kg ha⁻¹, and GEA 1499 at 5 kg ha⁻¹) on various aspects of muskmelon growth and yield.
The findings were striking. The combination of 100% P₂O₅ with GEA 1499 at 2.5 kg ha⁻¹ significantly improved leaf count, vine length, photosynthesis, stomatal conductance, transpiration, chlorophyll index, marketable yield, and total soluble solids. Moreover, it reduced undesirable traits such as rind thickness and seed cavity dimensions, indicating a marked improvement in fruit quality.
“Phosphorus enhances gas exchange via ATP and the Calvin cycle, while biostimulants containing microbes and plant extracts improve nutrient availability,” explained Balusamy. “This synergistic effect promotes better muskmelon growth, yield, and fruit quality.”
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. As the global population grows and agricultural land becomes increasingly scarce, the need for sustainable and efficient farming practices becomes ever more critical. Biostimulants offer a promising solution, enhancing crop productivity without relying on synthetic fertilizers or pesticides.
The study’s findings suggest that farmers could significantly boost their yields and improve fruit quality by adopting biostimulants in conjunction with optimal phosphorus levels. This could lead to increased profitability and sustainability in muskmelon production, benefiting both farmers and consumers.
Looking ahead, this research could pave the way for further exploration into the use of biostimulants in other crops and regions. As Balusamy noted, “The combination of plant extracts provides phytohormones that complement the microbial action and improve the overall efficiency of the biostimulant.” This opens up new avenues for developing more effective and tailored biostimulant formulations.
In conclusion, this study highlights the potential of biostimulants to revolutionize sustainable agriculture. By enhancing phosphorus use efficiency and improving crop yield and quality, biostimulants offer a viable solution to some of the most pressing challenges facing the agriculture sector today. As research in this field continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective solutions emerging, shaping the future of farming for generations to come.