In a significant stride for legume crop improvement, researchers have unveiled a high-quality genome assembly for the adzuki bean (Vigna angularis), coupled with a comprehensive genetic variation map. This breakthrough, published in *Advanced Science*, promises to revolutionize breeding programs and enhance the commercial potential of this globally important crop.
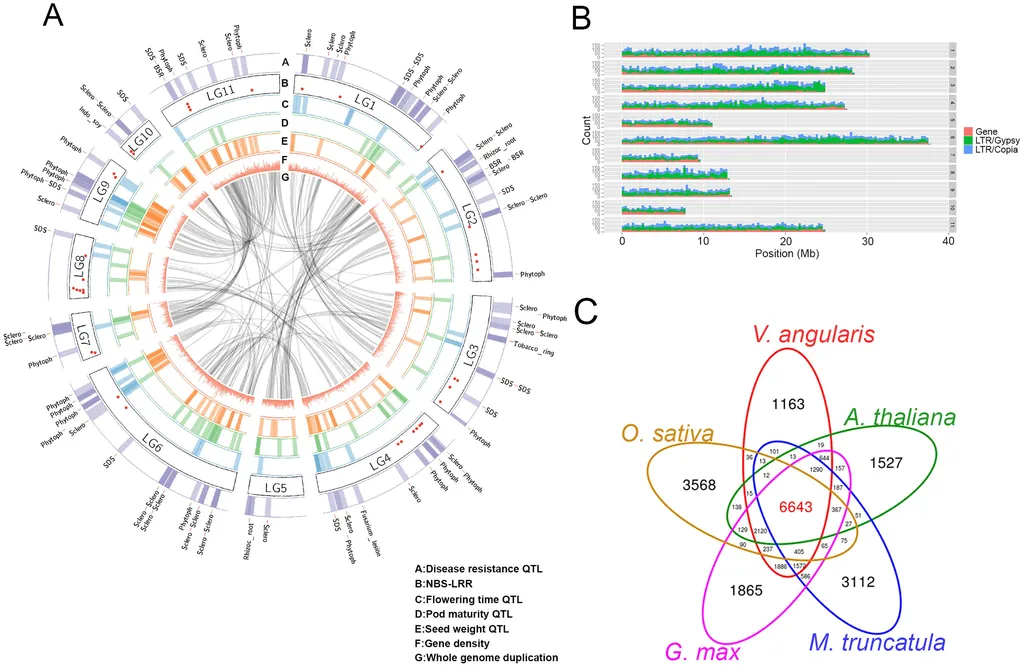
The study, led by Liangliang Hu from the State Key Laboratory of Crop Gene Resources and Breeding at the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, addresses critical bottlenecks in adzuki bean breeding. By resequencing 546 diverse adzuki bean accessions, the team constructed a detailed genetic variation map, revealing distinct population structures and identifying genomic variations linked to key agronomic traits.
“Our findings provide a valuable foundation for understanding adzuki bean diversity and pave the way for more targeted breeding strategies,” said Hu. The research pinpointed 251 loci significantly associated with eight key agronomic traits, including seed coat color, size, shape, and flowering time. Notably, candidate genes such as ANKRD50 and NAC73 were identified for seed morphology, ANR1 for flavonoid content, and NPF5.4 for flowering time.
The insights gleaned from this study extend beyond trait mapping. Comparative genomics analyses offer a glimpse into the domestication processes of the adzuki bean, shedding light on its evolutionary history and adaptation. This information is invaluable for breeders seeking to enhance yield, quality, and resilience in adzuki bean varieties.
To facilitate the practical application of these findings, the researchers developed AdzukiBeanAtlas, a versatile, user-friendly toolkit. This cross-platform resource enables molecular marker development and accelerates breeding programs by providing easy access to genomic data and analysis tools.
The commercial implications of this research are substantial. Adzuki beans are a staple in many cuisines and are valued for their nutritional content and versatility. Enhanced breeding programs can lead to improved varieties with better yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to diverse environments. This, in turn, can boost the agricultural sector by increasing productivity and marketability.
As the global demand for sustainable and nutritious food sources grows, the insights and tools provided by this study are timely and relevant. By leveraging high-resolution genomic resources, breeders can develop adzuki bean varieties that meet the evolving needs of farmers and consumers alike.
The integration of genomic data with practical breeding tools marks a significant step forward in precision breeding. This approach not only enhances the efficiency of breeding programs but also ensures that the genetic diversity of adzuki beans is fully utilized. The future of adzuki bean cultivation looks promising, with the potential for improved varieties that can thrive in various climatic conditions and resist pests and diseases.
In summary, this research represents a major advancement in the field of crop genomics and breeding. The high-quality genome assembly, comprehensive genetic variation map, and the development of AdzukiBeanAtlas provide a robust foundation for the genetic improvement of adzuki beans. These resources will undoubtedly accelerate breeding programs and contribute to the sustainable production of this important legume crop.